External secrets manager
Overview
The External Secrets Manager page helps you integrate and manage external secrets from AWS and Azure within the Cinchy platform.
Prerequisites
To use the External Secrets Manager, it's important to have the following:
- Working knowledge of how to configure secrets on either AWS or Azure platforms.
- An understanding of the Cinchy secrets manager.
Supported types
The External Secrets Manager supports the following types of authentication from AWS and Azure:
AWS
The IAM role must be assigned to the web pod the same way it is done for connections.
Azure
- Managed identities (when Cinchy Web is hosted on Azure)
- Registered applications
Table overview
The External Secrets Manager table has the following unique columns:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Unique name of the external secret. |
| Type | Lists the platform type of the secret. Options include AWS Secrets Manager or Azure Key Vault. |
| Parameters JSON | The JSON object that contains the mandatory information for each secret type. Refer to the JSON requirements section for more details. |
| Read Groups | The Cinchy Groups that have read access to the record. |
| Write Groups | The Cinchy Groups that have write access to the record. |
| ID | The auto-generated GUID. |
| ID Override | The value you enter into this field will override ID. |
| Sync GUID | The Sync GUID is used to facilitate DXD Workflows. |
| Description | Useful to help others understand the usage/purpose of the secret. |
Parameters JSON
Each secret type has a JSON schema (Parameters JSON) that must be filled with mandatory values. Select the tabs below for a description and example of each JSON schema.
- AWS Access Key
- AWS IAM Role
- Azure Managed Identity
- Azure Registered Application
| Key | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
authType | Mandatory. Indicates the type of authentication used. "AWS Access Key" signifies the use of an AWS Access Key for authentication. | "AWS Access Key" |
parameters | A nested JSON object containing specific configuration details. | |
region | Mandatory. Specifies the AWS region. | "ca-central-1" |
accessKey | Mandatory. The AWS Access Key ID, part of the credentials used to authenticate and authorize AWS service requests. | "AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE" |
secretAccessKey | Mandatory. The Secret Access Key associated with the Access Key ID, used for secure AWS service requests. | "wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY" |
Access key example
{
"authType": "AWS Access Key",
"parameters": {
"region": "ca-central-1",
"accessKey": "AKIAIOSFODNN7EXAMPLE",
"secretAccessKey": "wJalrXUtnFEMI/K7MDENG/bPxRfiCYEXAMPLEKEY"
}
}
| Key | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
authType | Indicates the type of authentication used. In this case, "AWS IAM Role" signifies the use of an AWS IAM Role. | "AWS IAM Role" |
parameters | A nested JSON object containing specific configuration details. | |
parameters.region | Specifies the AWS region. "ca-central-1" denotes the Canada Central region. | "ca-central-1" |
parameters.roleArn | The Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the IAM role. | "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/MyExampleRole" |
AWS IAM Role example
{
"authType": "AWS IAM Role",
"parameters": {
"region": "ca-central-1",
"roleArn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/MyExampleRole"
}
}
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
authType | Indicates the authentication method used. | "Azure Managed Identity" |
parameters | A nested JSON object for specific configuration details. | |
parameters.managedIdentityClientId | The client ID of the managed identity. | "87654321-4321-4321-4321-210987654321" |
parameters.url | The URL pointing to an Azure resource or service where the managed identity is used. | "https://example.azurewebsites.net" |
Azure Managed Identity example
{
"authType": "Azure Managed Identity",
"parameters": {
"managedIdentityClientId": "87654321-4321-4321-4321-210987654321",
"url": "https://example.azurewebsites.net"
}
}
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
authType | Indicates the authentication method used. | "Azure Registered Application" |
parameters | A nested JSON object for specific configuration details. | |
parameters.clientId | The unique identifier for the registered application in Azure. | "12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789abc" |
parameters.clientSecret | The secret key associated with the registered application, used for authentication. | "zYxwVuTsRqPoNmLk1234567890" |
parameters.tenantId | The unique identifier for the Azure Active Directory tenant associated with the application. | "87654321-4321-4321-4321-210987654321" |
parameters.url | The URL associated with the registered application, potentially pointing to a hosted endpoint or resource within Azure. | "https://example.azure.com" |
Azure Registered Application example
{
"authType": "Azure Registered Application",
"parameters": {
"clientId": "12345678-1234-1234-1234-123456789abc",
"clientSecret": "zYxwVuTsRqPoNmLk1234567890",
"tenantId": "87654321-4321-4321-4321-210987654321",
"url": "https://example.azure.com"
}
}
Create AWS Secret Manager secrets
Follow these steps to create secrets in the AWS Secret Manager.
- Open AWS Secret Manager.
- Navigate to Secrets > Store a new secret > Other type of secret.
- Add in your keys, values, secret name, and other other relevant fields.
Cinchy environment settings secrets
- Open AWS Secret Manager.
- Navigate to Secrets > Store a new secret > Other type of secret.
- Add the following keys and values:
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
encryptionkey | Your encryption key, set to random 32-byte value in a 64-character hexadecimal string format. This should only be set on initial environment creation, and cannot be rotated thereafter. |
connectionspassword | The connections@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
workerpassword | The worker@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
eventlistenerpassword | The eventlistener@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
maintenancepassword | The maintenance@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
cinchyautomationspassword | The automations@cinchy.com user account password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
- Update the
Secret Nameas follows:cinchy-environment-settings-<cinchy_instance_name>, for examplecinchy-environment-settings-<development>.
- Update other fields as needed.
Additional AWS Secret Manager Secrets
Use the below to create additional secrets, using your own instance name where indicated.
- The initial Secret Value will be the content of the relevant JSON of
cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations\<cluster_name>\<cinchy_instance_name>\secrets
| Key | Secret Name |
|---|---|
| 'orchestrationautomationrunnersecretappsettings' | orchestration-automationrunner-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
| 'orchestrationautomationrunnersecretconfig' | orchestration-automationrunner-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> |
| 'orchestrationschedulersecretconfig' | orchestration-scheduler-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> |
connectionssecretconfig | connections-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> |
connectionssecretappsettings | connections-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
eventlistenersecretappsettings | event-listener-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
formssecretconfig | forms-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> |
maintenanceclisecretappsettings | maintenance-cli-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
workersecretappsettings | worker-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
websecretappsettings | web-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
If SSO is enabled:
| Key | Secret Value | Secret Name |
|---|---|---|
idpsecretappsettings | The content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations\<cluster_name>\<cinchy_instance_name>\secrets | idp-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
idpsecretmetadata | SSO metadata.xml content | idp-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> |
Create Azure Key Vault secrets
Follow these steps to create secrets in Azure Key Vault.
- Navigate to your Key Vault in the Azure portal.
- Open Key Vault Objects > Secrets.
- Click Generate/Import.
- Input your secret name and value.
- Select Create.
Additional Azure Key Vault Cinchy secrets
- Navigate to your Key Vault in the Azure portal.
- Open Key Vault Objects > Secrets.
- Click Generate/Import.
- On the Create a Secret screen, choose the following values:
- Upload options: Manual.
- Content Type: JSON
- Name and Value: Choose the secret name and value from the below list, replacing 'cinchy_instance_name' where indicated:
Environment settings
| Key | Value |
|---|---|
encryptionkey | Your encryption key, set to random 32-byte value in a 64-character hexadecimal string format. This should only be set on initial environment creation, and cannot be rotated thereafter. |
connectionspassword | The connections@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
workerpassword | The worker@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
eventlistenerpassword | The eventlistener@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy.. |
maintenancepassword | The maintenance@cinchy.com service account user password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy.. |
cinchyautomationspassword | The automations@cinchy.com user account password. A unique value should be set for each environment. Password can be rotated per your password policy. |
Additional secrets:
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
worker-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
web-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
maintenance-cli-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
idp-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
forms-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
event-listener-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
connections-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
connections-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
idp-secret-metadata-<cinchy_instance_name> (Note: This is an additional secret only required when sso_enabled=true in the azure.json file) | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
orchestration-automationrunner-secret-appsettings-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
orchestration-automationrunner-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
orchestration-scheduler-secret-config-<cinchy_instance_name> | The value for the secret will be the content of the relevant JSON of cinchy.kubernetes\environment_kustomizations<cluster_name><cinchy_instance_name>\secrets |
- Leave the other values to their defaults.
- Select Create.
Set up an external secret
To set up an external secret, do the following:
Configure your secret
- Create your secret using the preferred platform and secret type (Create an AWS Secrets Manager secret, Create Azure Key Vault Secret).
- In the External Secrets Manager table, enter a unique name for your configuration.
- Select the platform type under the Type column.
- Select a JSON schema from the JSON schema section and enter the mandatory information for your secret.
- Copy the schema into the Parameters JSON column.
Use external secrets in Cinchy
To use the external secrets from the External Secrets Manager table as secrets in Cinchy, such as in a data sync, do the following:
- In the Secrets table, select the External view.
- In the Secret Source column, select "External".
- Select a Domain and enter a Name for your secret.
- In the External Secret Manager column, select the ID or unique name of your external secret.
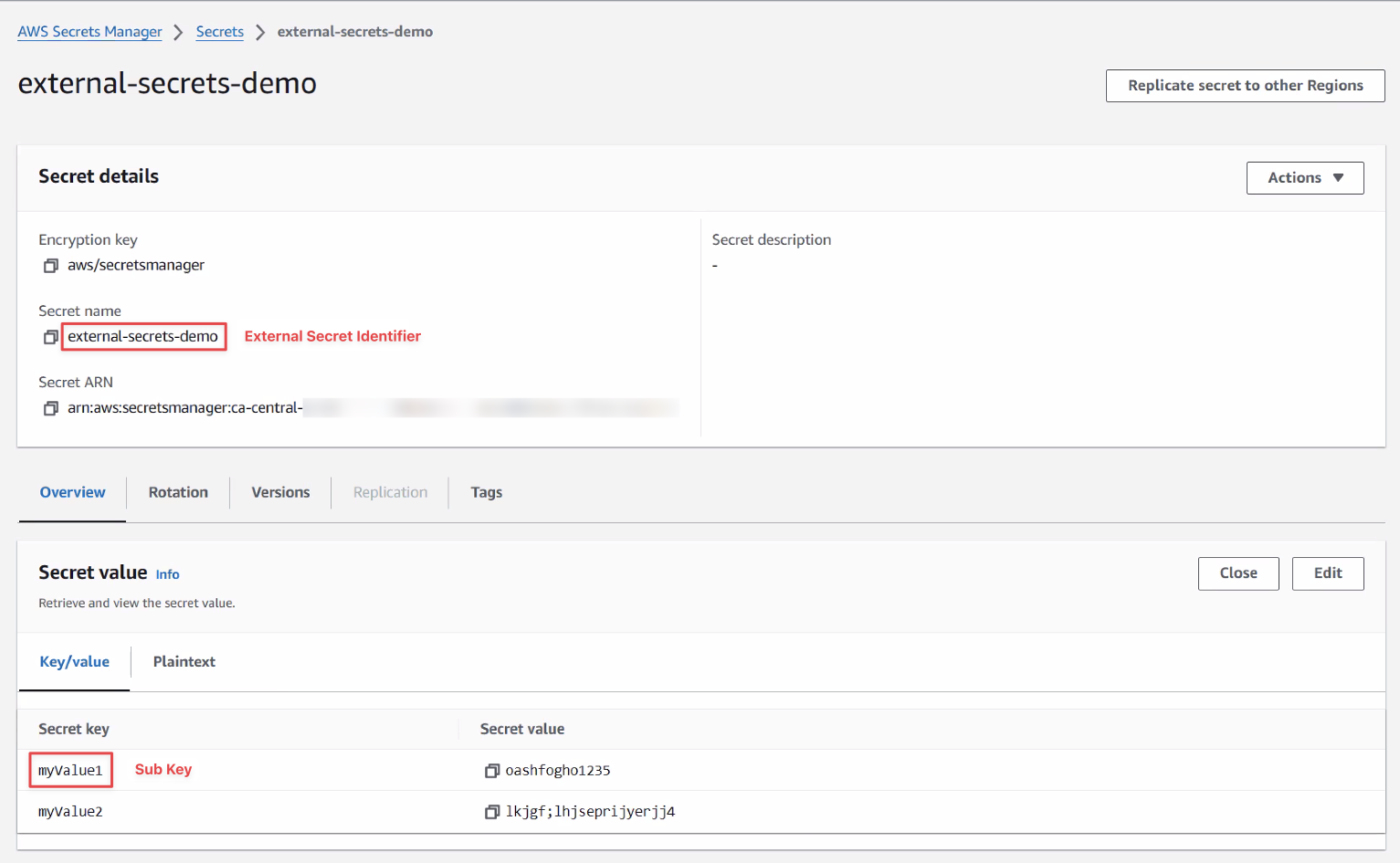
- In the External Secret Identifier column, enter the name of the secret as it appears in AWS or Azure.
- If your secret consists of multiple key value pairs, enter the name of the key for this secret in the Sub Key column.
Use encrypted parameters
The External Secrets Manager table also supports encrypted versions of your field, such as a secret access key.
To use an encrypted version, do the following:
- Use the Worker CLI
--encryptcommand on your target parameter. - Copy the value of into the target JSON parameter.
For more information, please see the CLI Command list