Cinchy functions
Overview
The Cinchy functions covered in this section are:
- resolveLink()
- currentUserID()
- currentUsersGroups()
- exec
- executeSavedQuery()
- GetLastModifiedBy()
- Draft
- Editable
- DELETE
- ISNULL
- NULLIF
- @@ROWCOUNT
- ROWCOUNT_BIG
Exec
exec can be used to execute a Saved Query.
Syntax
exec [Domain].[Saved Query Name]
Example
The below example executes the 'Update Country' saved query.
exec [Documentation].[Update Country]

resolveLink()
Use the resolveLink function to insert or update values for link columns. Use it with values in the target table or the Cinchy Id.
Using resolveLink against non-unique data values may not return the same data response each time; in that scenario we recommend that you resolve using the CinchyID instead.
Syntax
ResolveLink('value(s)','column in target table')
'CinchyId,0,CinchyId2,0'
Example
INSERT INTO [Cinchy].[Domain] (Name, Colour)
VALUES ('Test', ResolveLink('Purple','Name'))
INSERT INTO [Corporate].[Projects] (Name, Teams)
VALUES ('CQL Documentation', ResolveLink('Customer Success, Product, Development','Name'))
UPDATE [Product].[Backlog]
SET [Watchers] = '152,0,187,0,347,0'
WHERE [Summary] = 'You can use resolveLink to update link values in DML.'
currentUserID()
currentUserID() returns the currently logged in user's CinchyId. This is useful for setting up views as well as permissions.
Return Type
This function returns the CinchyId value.
Syntax
currentUserID()
Example 1
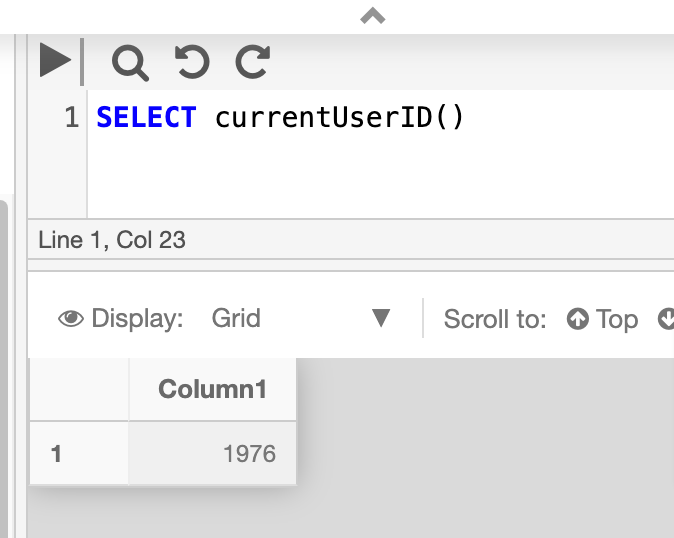
The below example returns the CinchyId of the logged in user.
SELECT currentUserID()
Example 2
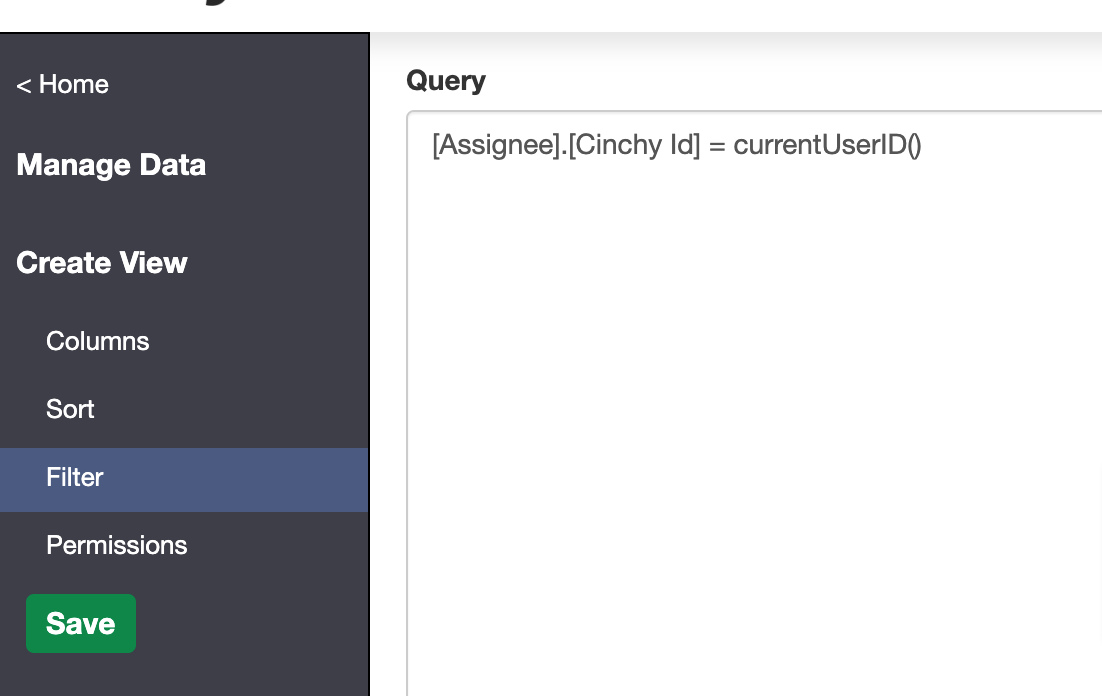
You can use the function when creating table views. In the below example, the view will filter and return only rows where the [Assignee] column is linked to the currently logged in user.
[Assignee].[Cinchy Id] = currentUserID()
currentUsersGroups()
currentUsersGroups() function returns a list of groups that the current user belongs to, including any parent groups. For example, if a
user is in the Cinchy Product group and the Cinchy Product group is under Cinchy Employees, then both will be returned.
Syntax
[Cinchy Id] IN (currentUsersGroups())
Example
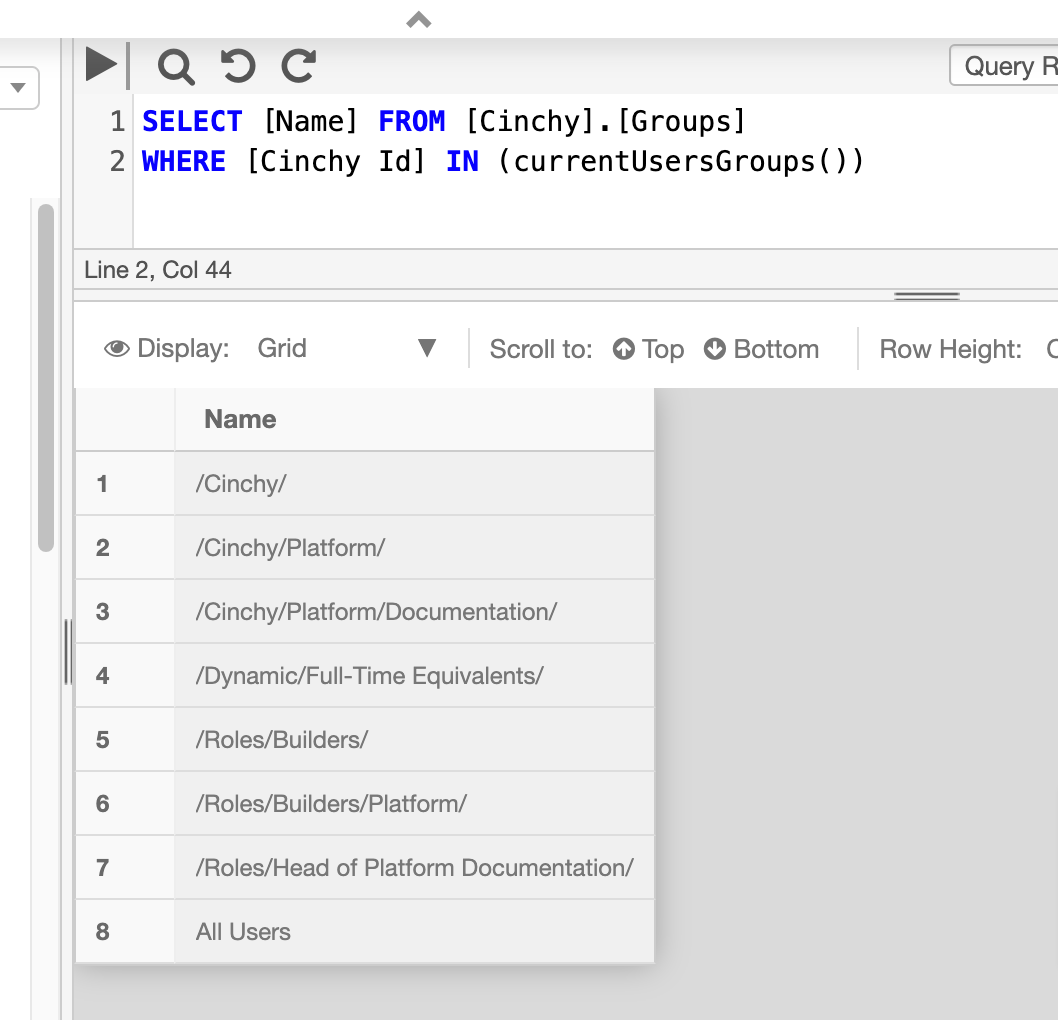
The below example returns the names of all groups that the currently logged in suse belongs to.
SELECT [Name] FROM [Cinchy].[Groups]
WHERE [Cinchy Id] IN (currentUsersGroups())
executeSavedQuery()
executeSavedQuery() returns a scalar or list of scalar values
from the saved query specified as the parameters of the function. This function
has two optional parameters: CacheTimeout and RecordLimitForReturn.
Syntax
[Column] = executeSavedQuery('Domain','Saved Query Name', timeout, recordlimit)
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
Domain | The name of the Domain in which the saved query belongs. | HR |
Saved Query Name | The name of the saved query. | Get Department |
timeout | Optional. Specifies a cache timeout, in seconds. | 30 |
recordlimit | Optional. This parameter limits the amount of records returned. For example, if the query returns 10 records, but you set the parameter to 5, then you will get the first five records back. | 5 |
Example 1
The below example executes the 'Get Department' saved query.
[Department] = executeSavedQuery('HR','Get Department',30, 5)
Example 2
The below example executed the 'Get My Direct Reports' multi-value saved query.
[Assignee] IN (executeSavedQuery('HR','Get My Direct Reports')
GetLastModifiedBy()
GetLastModifiedBy returns the CinchyID of the user who last modified the specified column. It's currently only supported in SELECT statements.
Return Type
This function returns the CinchyID of the relevant user.
Syntax
GetLastModifiedBy([Column])
Example
This example will return the CinchyID of the user who last modified the Name column in the Employees table.
SELECT getLastModifiedBy([Name])
FROM [HR].[Employees]
Draft
Draft `queries for draft values on tables where Change Approval is enabled.
When querying for draft data, the query result type needs to be set to "Query Results (including Draft Data)"
Syntax
SELECT draft([Column])
FROM [Domain].[Table]
Example
In this example, we want to query all data in the Employees table, including the data that's pending in a change request.
To return results that include the draft changes in the First Name column, set your query builder results to Include Draft Data, and use the following syntax:
SELECT [Employee ID], draft([First Name]), [Full Name], [Salary], [Date Hired]
FROM [HR].[Employees]
Editable
Editable can be used in tandem with a SELECT statement to check whether the user executing the query has edit access to a specific record.
Edit access is a permission set in the Data Controls > Entitlements menu of a table that provides granular, cell-level access controls.
Return Type
This function will return a 1 if the executing user has edit access to the cell, and a 0 if not.
Syntax
SELECT [column], EDITABLE([column]) as 'alias'
FROM [domain].[table]
Example
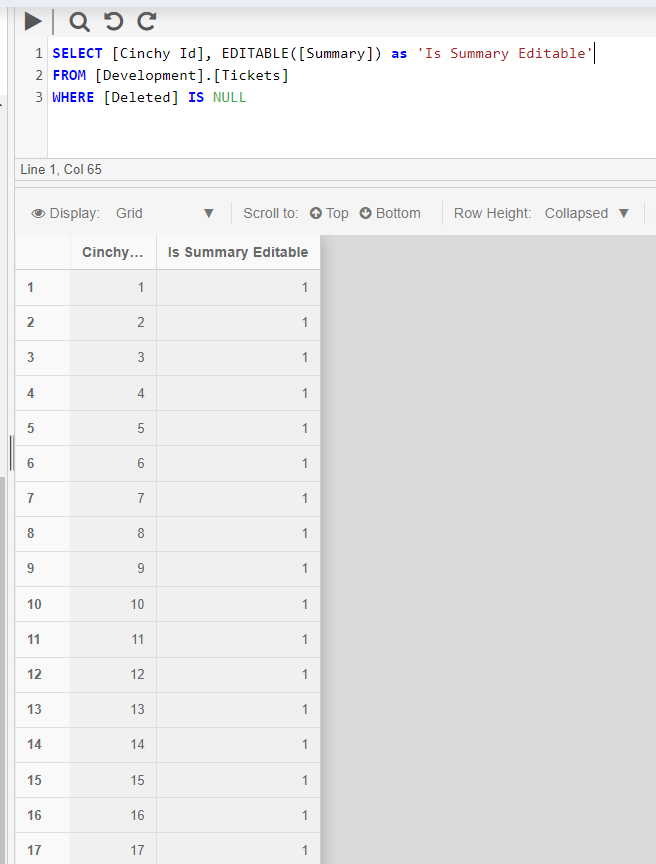
This example queries the [Summary] column of the [Development].[Tickets] table. The entitlements rules set on the table allow the user edit access to any record where the [Cinchy Id] > 100.
Any record where the value of the [Cinchy Id] column is equal to or less than 100 will return a result of 1, meaning editable, in the Is summary editable column.
SELECT [Cinchy Id], EDITABLE([Summary]) as 'Is Summary Editable'
FROM [Development].[Tickets]
DELETE
DELETE can delete a row or group of rows from a table. Ensure that you change your query type to "Number of Rows Affected" in the Cinchy Query builder when running this command.
Syntax
DELETE FROM
Example 1
This example will delete all rows from the [Customer].[Customer Tickets] table
DELETE FROM [Customer].[Customer Tickets]
Example 2
This example will delete all rows from the [Customer].[Customer Tickets] table that match the WHERE statement.
DELETE FROM [Customer].[Customer Tickets]
WHERE Status = 'Closed'
ISNULL
ISNULL checks for NULL values in an expression and replaces them (in the query results, not in the table itself) with a replacement expression.
Return Type
Returns the same type as the check expression.
Syntax
ISNULL ( check_expression , replacement_value )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
check_expression | The expression to be checked for NULL values. | Status |
replacement_value | A value that will replace the NULL. | 'Not Started' |
Example
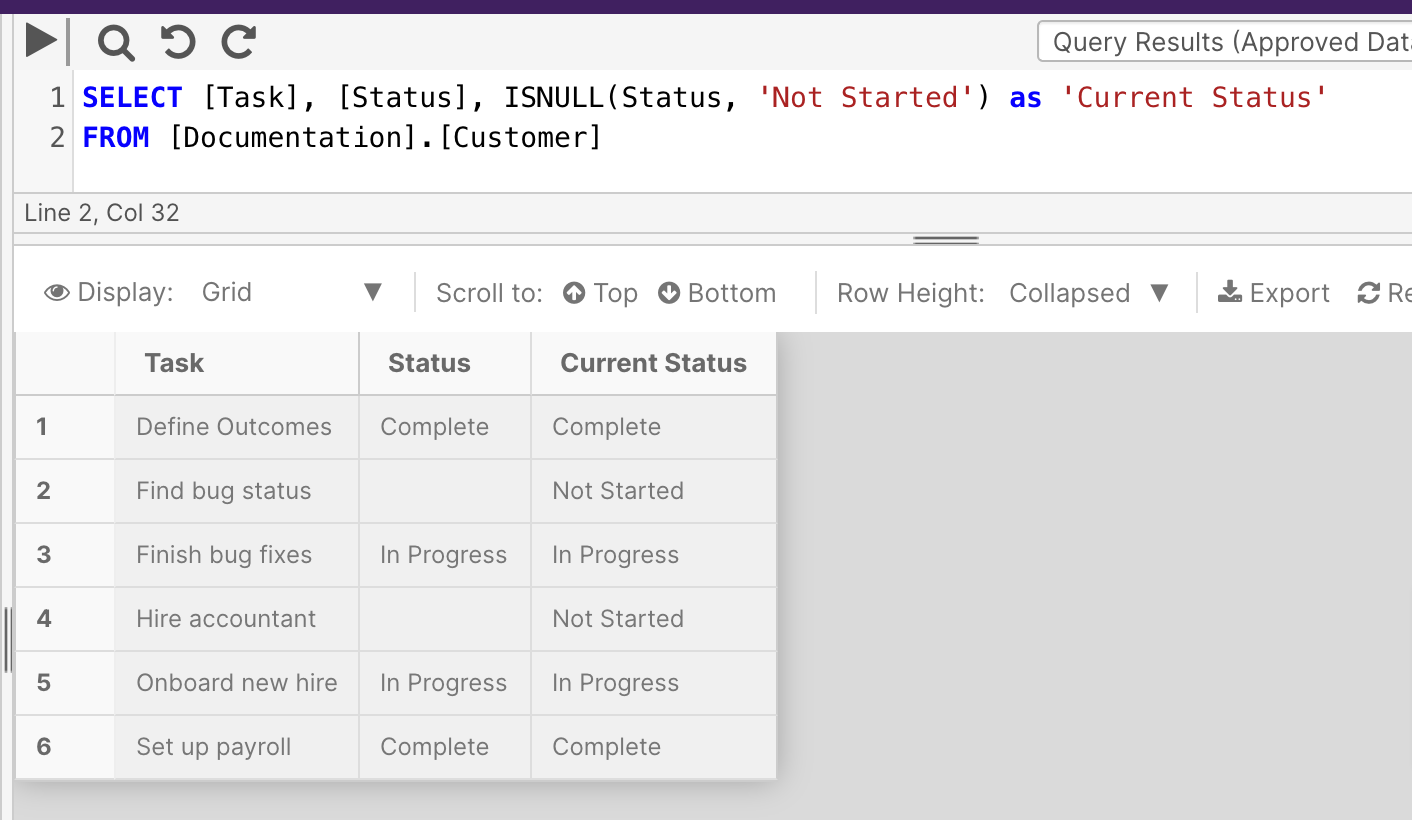
This example checks the 'Status' column for NULL values. When found, the query results replace those records with 'Not Started'.
SELECT [Task], [Status], ISNULL(Status, 'Not Started') as 'Current Status'
FROM [Documentation].[Customer]
ISNUMERIC
ISNUMERIC checks whether an expression is a valid numeric type.
Return Type
This function returns a 1 when the expression evaluates to a valid numeric data type, and returns a 0 otherwise.
Syntax
ISNUMERIC (expression)
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | An expression or column that the function will evaluate against. | Price |
Example
This example checks whether the 'Price' column of the [Sales].[Products] table contains numeric data types.
SELECT ISNUMERIC (Price)
FROM [Sales].[Products]
NEWID
NEWID creates a unique value of type uniqueidentifier.
Return Type
uniqueidentifier
Syntax
NEWID ()
Example
This example uses the NEWID function to randomly query a single result from the [Documentation].[Customer] table.
SELECT TOP 1[Customer ID], [Name]
FROM [Documentation].[Customer]
ORDER BY NEWID()
NULLIF
NULLIF returns a null value if the two specified expressions in the query are equal. If unequal, it will return the value of expression_1.
Syntax
NULLIF ( expression_1 , expression_2 )
Example 1
The following example contains two equal expressions. The query will return a null value.
SELECT NULLIF (110, 110 )
Example 2
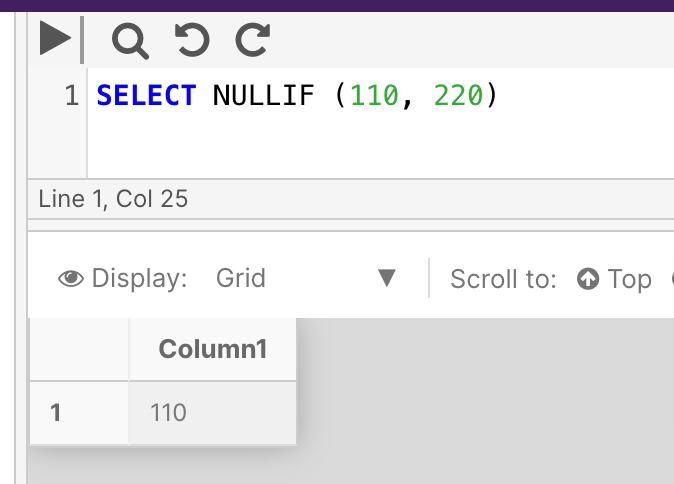
The following example contains two non-equal expressions. The query will return expression_1 as the result to indicate as such.
SELECT NULLIF (110, 220)
@@ROWCOUNT
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
@@ROWCOUNT Returns the number of rows affected by the last statement executed.
Return Type
int
Syntax
@@ROWCOUNT
Example
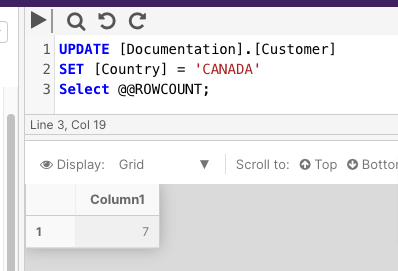
The following example updates the [Documentation].[Customer] customer to SET the Country column to Canada. The @@ROWCOUNT function is then used to return the number of columns that were affected by the update.
UPDATE [Documentation].[Customer]
SET [Country] = 'CANADA'
Select @@ROWCOUNT;
ROWCOUNT_BIG
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
ROWCOUNT_BIG Returns the number of rows affected by the last statement executed. It works similar to @@ROWCOUNT, but it returns bigint values.
Return Type
bigint
Syntax
ROWCOUNT_BIG ( )
Example
The following example updates the [Documentation].[Customer] customer to SET the Country column to Canada. The ROWCOUNT_BIG function is then used to return the number of columns that were affected by the update.
UPDATE [Documentation].[Customer]
SET [Country] = 'CANADA'
Select ROWCOUNT_BIG();