Modify Date and Time values
Overview
The modify date and time value functions covered in this section are:
DATEADD
The DATEADD function adds a specified number value to a specified datepart of an input date value, and then returns that modified value.
Syntax
DATEADD (datepart , number , date )
Return Type
The return value data type for this method is dynamic. The return type depends on the argument supplied for date. If the value for date is a string literal date, DATEADD returns a datetime value. If another valid input data type is supplied for date, DATEADD returns the same data type. DATEADD raises an error if the string literal seconds scale exceeds three decimal place positions (.nnn) or if the string literal contains the time zone offset part.
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
datepart | The part of a date to which the number will be added. | month |
number | An integer (or an expression that can resolve to an integer) that will be added. This integer can be a user-defined variable. It will truncate a specified number value that has a decimal fraction. | 2 |
date | An expression that can resolve to one of the following values: date, datetime, datetimeoffset, datetime2, smalldatetime, time | 2017-08-25 |
Example 1
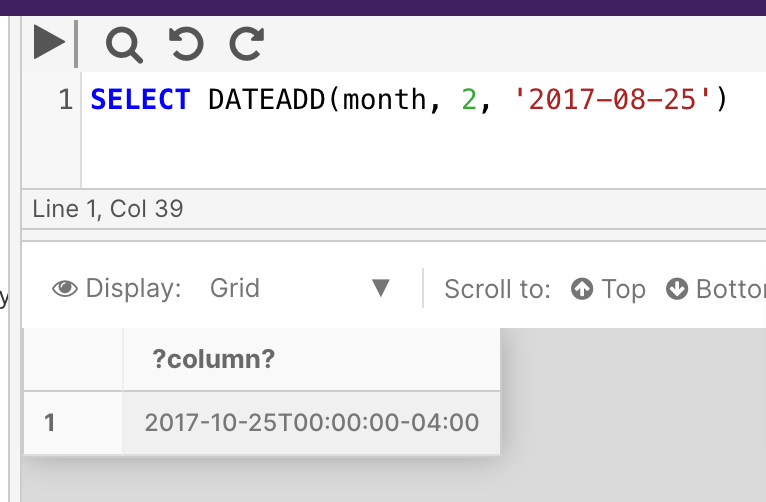
The below example increments the date 2017-08-25 by two months.
SELECT DATEADD(month, 2, '2017-08-25')
Example 2
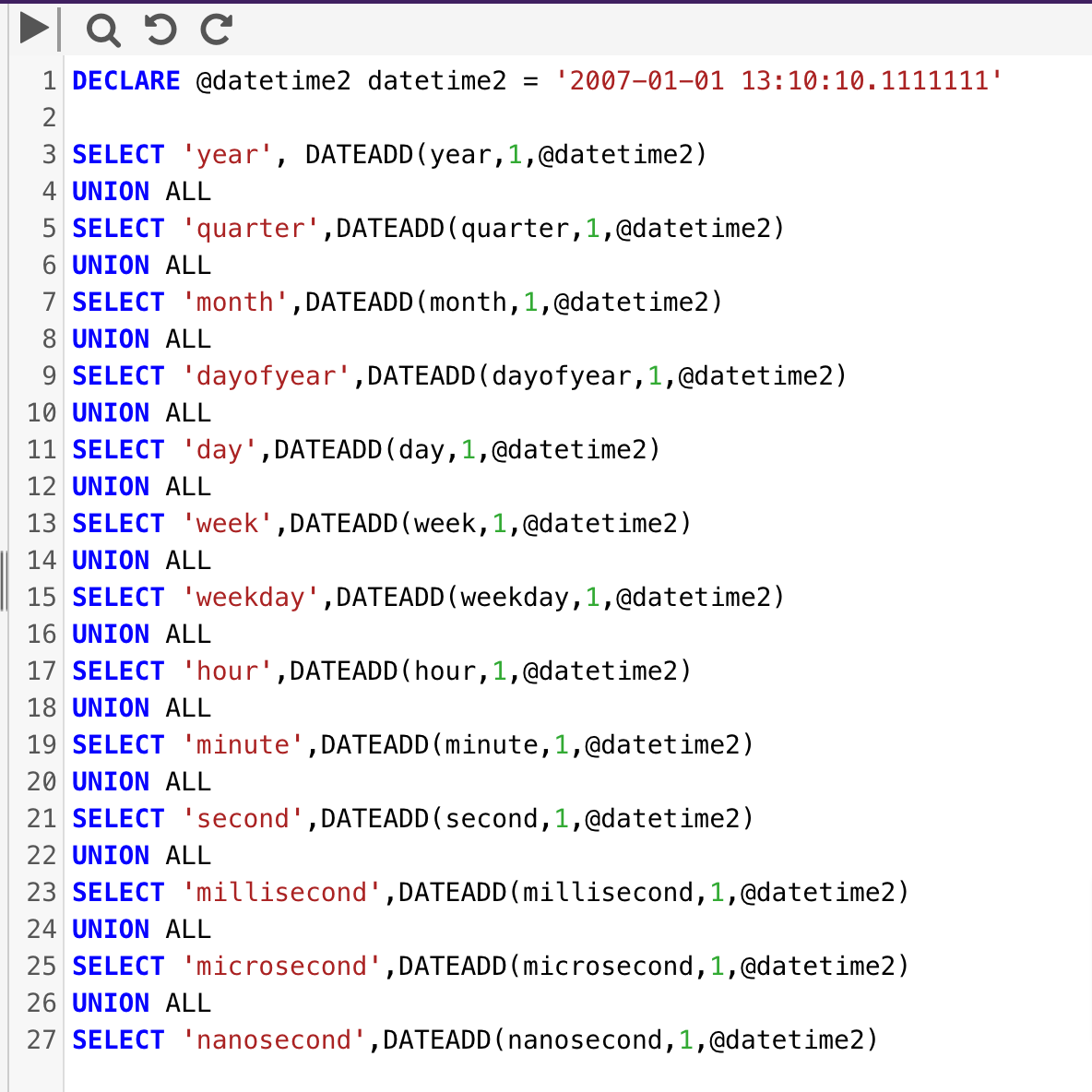
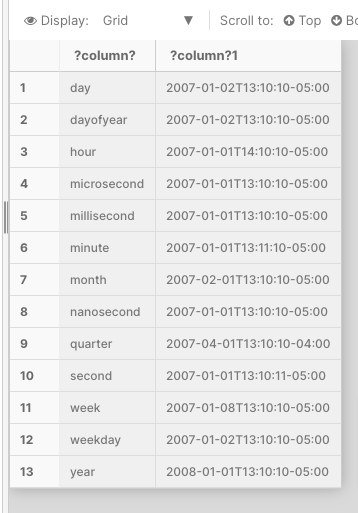
The below example increments the datepart by an interval of 1
DECLARE @datetime2 datetime2 = '2007-01-01 13:10:10.1111111'
SELECT 'year', DATEADD(year,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'quarter',DATEADD(quarter,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'month',DATEADD(month,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'dayofyear',DATEADD(dayofyear,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'day',DATEADD(day,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'week',DATEADD(week,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'weekday',DATEADD(weekday,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'hour',DATEADD(hour,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'minute',DATEADD(minute,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'second',DATEADD(second,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'millisecond',DATEADD(millisecond,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'microsecond',DATEADD(microsecond,1,@datetime2)
UNION ALL
SELECT 'nanosecond',DATEADD(nanosecond,1,@datetime2)
Example 3
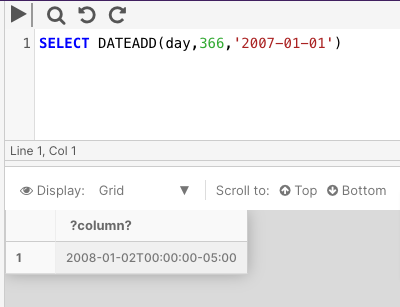
The below example increments more than one level of datepart in a statement.
This query increments the day value by 365, a large enough number to also increment the year value of the date.
SELECT DATEADD(day,366,'2007-01-01')
Example 4
The below example uses expressions as arguments for the number and date parameters
This example adds 2 (two) days to each value in the OrderDate column, to derive a new column named PromisedShipDate:
SELECT
[Order Number],
[Order Date],
DATEADD(day, 2, [Order Date]) AS [Promised Ship Date]
FROM
[Sales].[Order Header]
WHERE
[Deleted] IS NULL
EOMONTH
EOMONTH returns the last day of the month containing a specified date, with an optional offset.
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform. Please check back at a later time. For a full list of in-progress function translations, see the CQL functions reference page.
Return Type
date
Syntax
EOMONTH ( start_date [, month_to_add ] )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
start_date | A date expression that specifies the date for which to return the last day of the month. | 12/1/2011 |
month_to_add | An optional integer expression that specifies the number of months to add to start_date. | 1 |
Remarks
EOMONTH can remote to SQL Server 2012 (11.x) servers and higher. It can't be remote to servers with a version lower than SQL Server 2012 (11.x).
Example 1
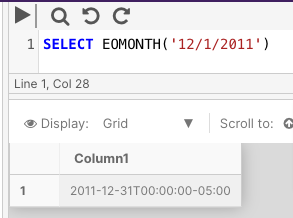
The following example returns the end of the month value for an explicit date (12/1/2011).
SELECT EOMONTH('12/1/2011')
Example 2
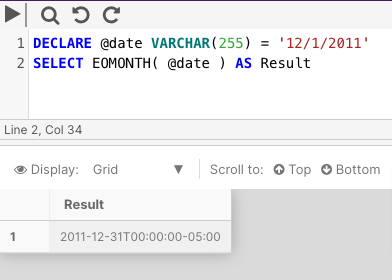
The following example converts a string parameter to VARCHAR(255) and returns its end of month value.
DECLARE @date VARCHAR(255) = '12/1/2011'
SELECT EOMONTH( @date ) AS Result
Example 3
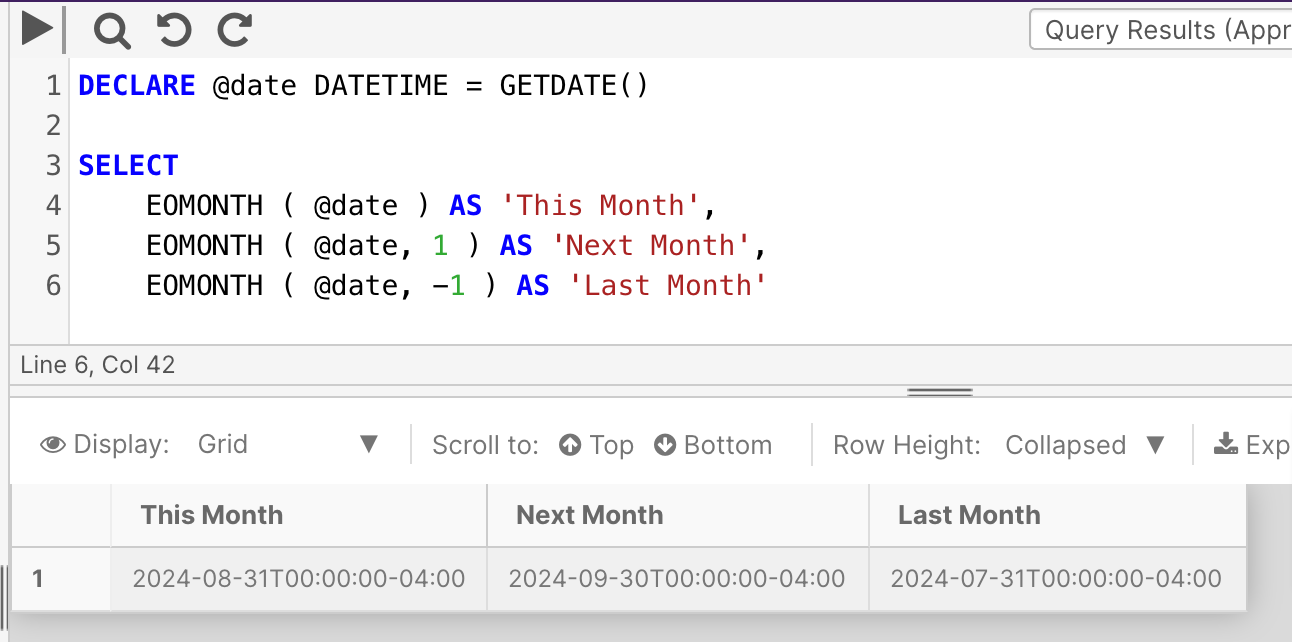
The following example will return three values relative to the current date, one without the month to add parameter, and two with (using both a negative and a positive integer amount).
DECLARE @date DATETIME = GETDATE()
SELECT
EOMONTH ( @date ) AS 'This Month',
EOMONTH ( @date, 1 ) AS 'Next Month',
EOMONTH ( @date, -1 ) AS 'Last Month'
SWITCHOFFSET
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform. Please check back at a later time. For a full list of in-progress function translations, see the CQL functions reference page.
SWITCHOFFSET can be used to return datetimeoffset values that have been changed from the stored time zone offset to a given new time zone offset.
Return Type
datetimeoffset
Syntax
SWITCHOFFSET ( expression, time_zone )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | An expression that can be resolved to a datetimeoffset(n) value. | 2023-09-20 |
time_zone | A character string in the format [+ | -]TZH:TZM or a signed integer (of minutes) that represents the time zone offset, and is assumed to be daylight-saving aware and adjusted. |
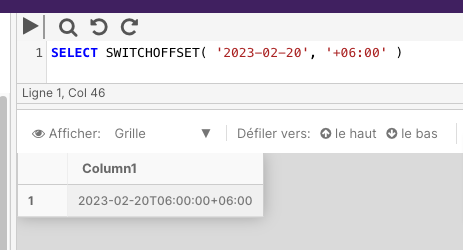
Example
SELECT SWITCHOFFSET( '2023-02-20', '+06:00' )
TODATETIMEOFFSET
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform. Please check back at a later time. For a full list of in-progress function translations, see the CQL functions reference page.
TODATETIMEOFFSET returns a datetimeoffset value that's translated from a datetime2 expression.
Return Type
datetimeoffset
Syntax
TODATETIMEOFFSET ( expression , time_zone )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | An expression that can be resolved to a datetime2 value. | 2023-02-20 02:33:18 |
time_zone | An expression that represents the time zone offset in minutes (if an integer), for example -120, or hours and minutes (if a string), for example '+13:00'. The range is +14 to —14 (in hours). The expression is interpreted in local time for the specified time_zone.. | -150 |
Example 1
Changing the time zone offset of the current date and time
The following example changes the zone offset of the current date and time to time zone -07:00.
DECLARE @todaysDateTime datetime2
SET @todaysDateTime = GETDATE()
SELECT TODATETIMEOFFSET (@todaysDateTime, '-07:00')
-- RETURNS 2019-04-22 16:23:51.7666667 -07:00
Example 2
Changing the time zone offset in minutes
The following example changes the current time zone to -120 minutes.
SELECT TODATETIMEOFFSET(SYSDATETIME(), -120)
-- RETURNS: 2019-04-22 11:39:21.6986813 -02:00
Example 3
Adding a 13-hour time zone offset
The following example adds a 13-hour time zone offset to a date and time.
SELECT TODATETIMEOFFSET(SYSDATETIME(), '+13:00')
-- RETURNS: 2019-04-22 11:39:29.0339301 +13:00