Mathematical functions
Overview
Mathematical functions perform calculations based on input values provided as parameters to the functions, and return numeric values.
The mathematical functions covered in this section are:
- ABS
- ACOS
- ASIN
- ATAN
- ATN2
- CEILING
- COS
- COT
- DEGREES
- EXP
- FLOOR
- LOG
- LOG10
- PI
- POWER
- RADIANS
- RAND
- ROUND
- SIGN
- SIN
- SQRT
- SQUARE
- TAN
ABS
ABS returns the absolute (positive) value of the specified numeric expression. (ABS changes negative values to positive values. ABS has no effect on zero or positive values.)
Syntax
ABS ( numeric_expression )
Return Type
Returns the same type as numeric expression
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
numeric_expression | A negative numeric expression. The function has no effect on zero or positive values. | -5.2 |
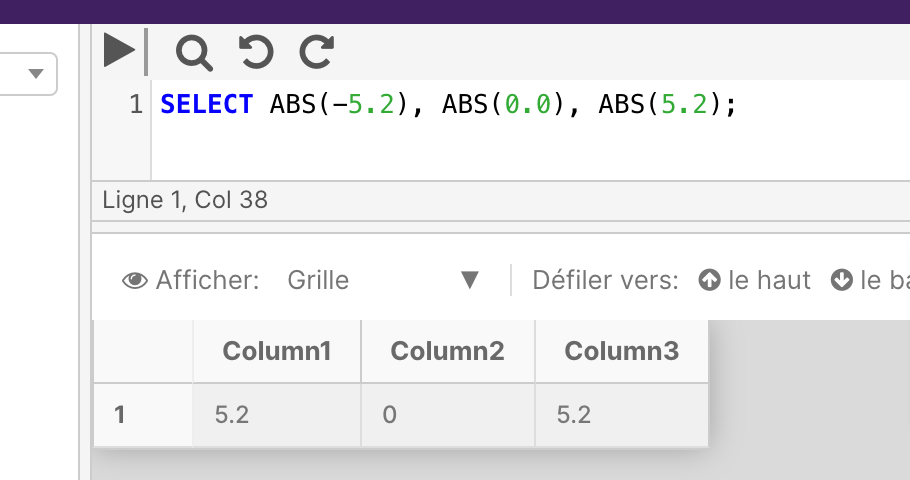
Example
The below example shows the results of using the ABS function on three different numbers.
SELECT ABS(-5.2), ABS(0.0), ABS(5.2);
ACOS
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
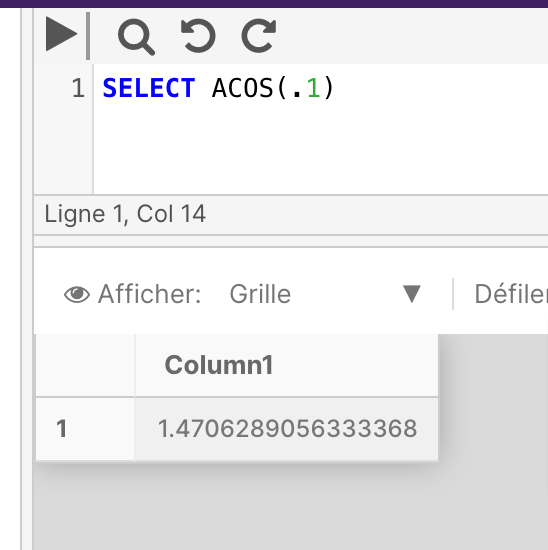
ACOS returns the angle, in radians, whose cosine is the specified float expression. This is also called arccosine.
Syntax
ACOS ( float_expression )
Return Type
float
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression of a value ranging from -1.00 to 1.00 | .1 |
Example
The below example returns the ACOS value of the specified angle.
SELECT ACOS(1)
ASIN
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
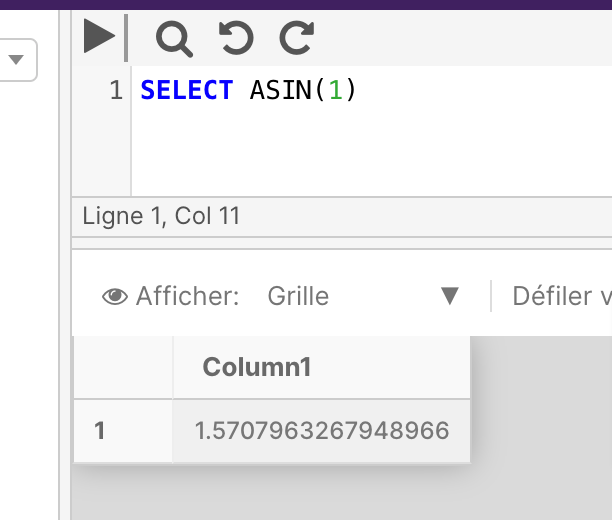
ASIN returns the angle, in radians, whose sine is that of a specified float expression. This is also called arcsine.
Syntax
ASIN ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression of a value ranging from -1.00 to 1.00 | 1 |
Return types
float
Example
The below example returns the ASIN value of the specified angle.
SELECT ASIN(1)
ATAN
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
ATAN returns the angle, in radians, whose tangent is a specified float expression. This is also called arctangent.
Syntax
ATAN ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression. | 1 |
Return Types
float
Example
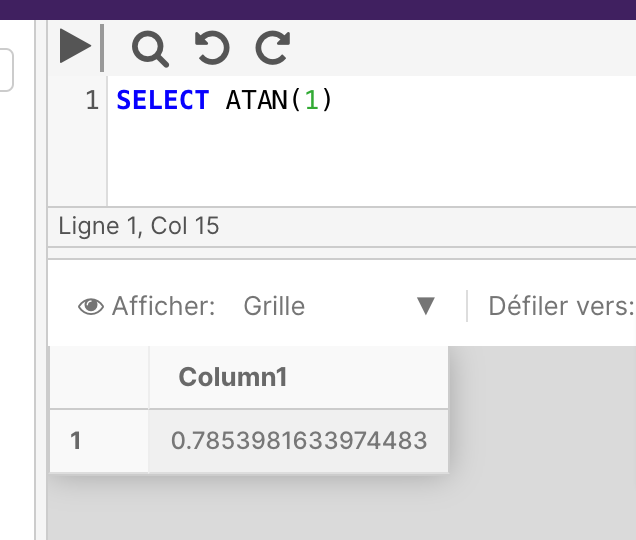
The below example returns the ATAN value of the specified angle.
SELECT ATAN(1)
ATN2
ATN2 returns the angle, in radians, between the positive x-axis and the ray from the origin to the point (y, x), where x and y are the values of the two specified float expressions.
Syntax
ATN2 ( float_expression , float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression. | 1 |
Return Types
float
Example
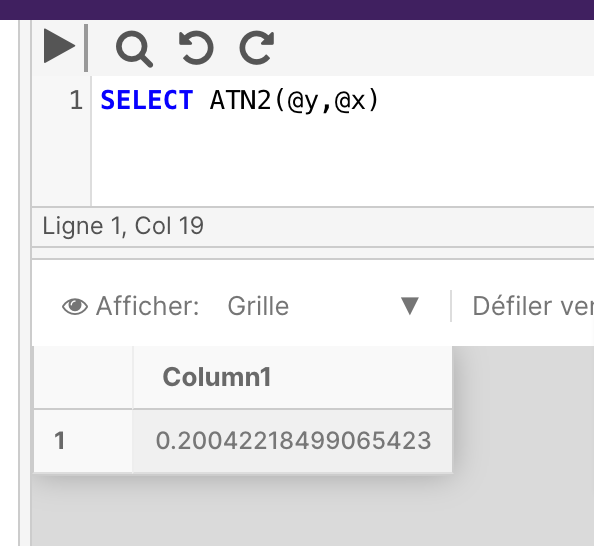
The below example calculates the ATN2 for the specified x and y components.
SELECT ATN2(@y,@x)
CEILING
CEILING returns the smallest integer greater than, or equal to, the specified numeric expression.
Syntax
CEILING ( numeric_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
numeric_expression | A numeric expression. Bit type is not supported | 1.2 |
Return Type
Return values have the same type as numeric_expression.
Example
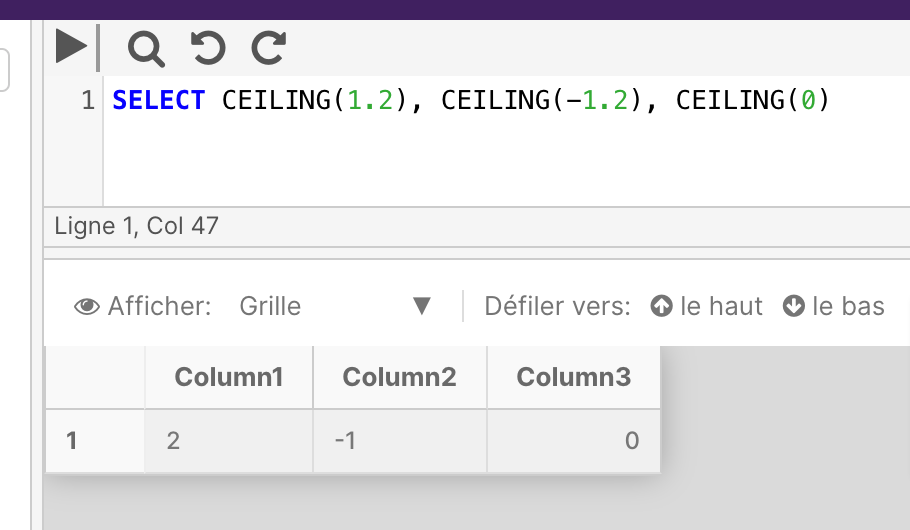
The below example shows positive numeric, negative numeric, and zero value inputs for the CEILING function.
SELECT CEILING(1.2), CEILING(-1.2), CEILING(0)
COS
COS returns the trigonometric cosine of the specified angle - measured in radians - in the specified expression.
Syntax
COS ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression. | 1 |
Return Type
float
Example
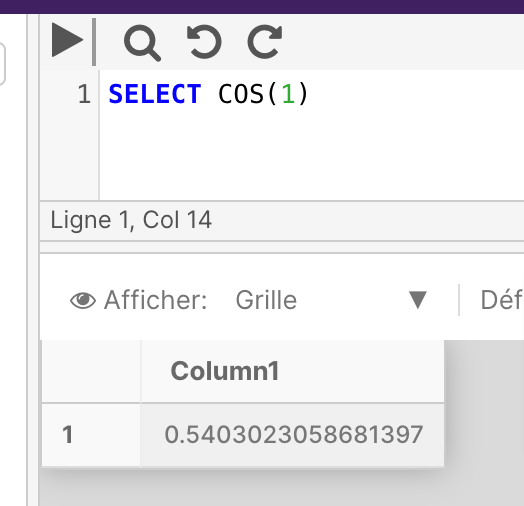
The below example returns the COS value of the specified angle.
SELECT COS(1)
COT
COT returns the trigonometric cotangent of the specified angle - in radians - in the specified float expression.
Syntax
COT ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression. | 1 |
Return Type
float
Example
This example returns the COT value for the specific angle.
SELECT COT(1)
DEGREES
DEGREES returns the corresponding angle, in degrees, for an angle specified in radians.
Syntax
DEGREES ( numeric_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
numeric_expression | A numeric expression. Bit type is not supported | 1.2 |
Return Type
Returns a value whose data type matches the data type of numeric_expression.
Example
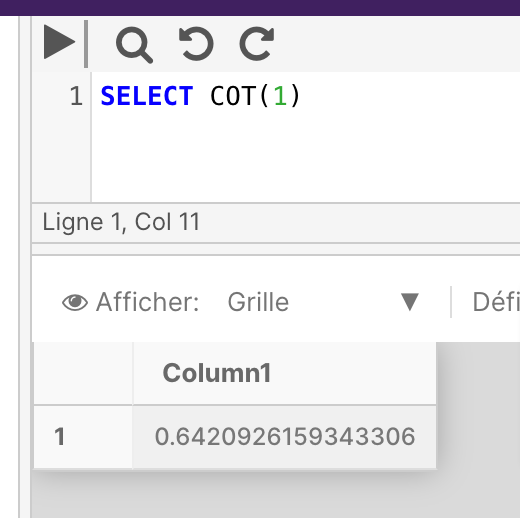
The below example returns the number of degrees in a specified radian.
SELECT DEGREES(1)
EXP
EXP returns e raised to the power of a specified number. The constant e (2.718281...), is the base of natural logarithms.
Syntax
EXP ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression. e will be raised to the power of this number. | 9 |
Return Type
float
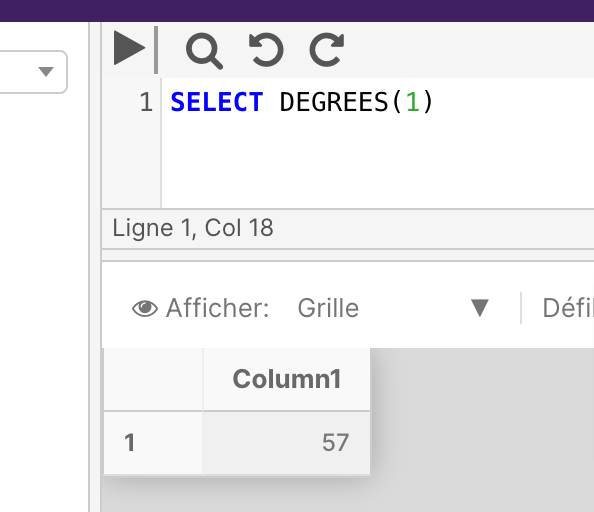
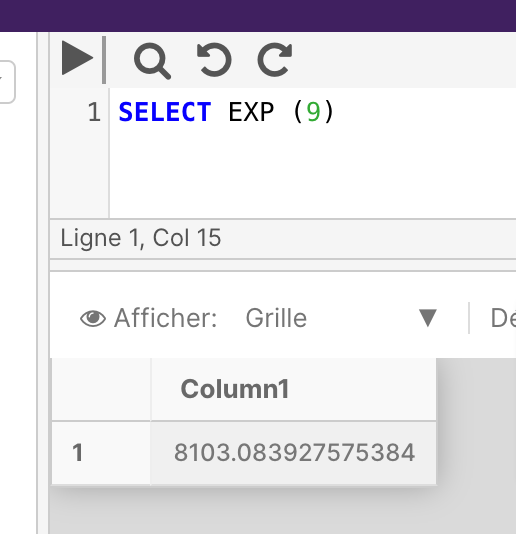
Example 1
SELECT EXP (9)
Example 2
The below example uses a compounding interest example to illustrate the use of EXP.
SELECT 'With continuous compounding interest, your principal amount of $'
+ @principal + ' will turn into $'
+ CONVERT(VARCHAR,@principal * EXP(@years * CAST(@interestRate AS FLOAT)))
+' after ' + @years + ' years at the interest rate of '
+ CONVERT(VARCHAR,CAST(@interestRate AS FLOAT) * 100) + '%'
FLOOR
FLOOR returns the largest integer less than or equal to the specified numeric expression.
Syntax
FLOOR ( numeric_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
numeric_expression | A numeric expression. Bit type is not supported | 1.2 |
Return Types
Returns the same type as numeric_expression.
Example
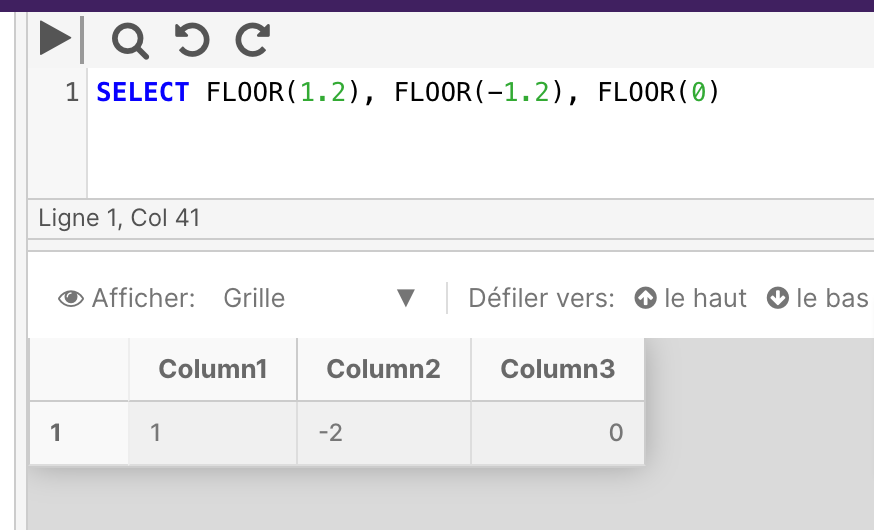
The following example shows positive numeric, negative numeric, and zero value inputs with the FLOOR function.
SELECT FLOOR(1.2), FLOOR(-1.2), FLOOR(0)
LOG
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
LOG returns the natural logarithm of the specified float expression.
Syntax
LOG ( float_expression [, base ] )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float type expression | 2 |
base | Optional. An integer argument (>1) that sets the base for the logarithm. | 4 |
Return Types
float
Example
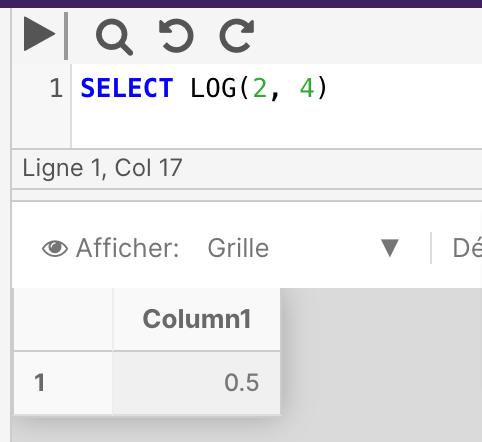
The below example returns the natural logarithm of 2 to a specified base (4):
SELECT LOG(2, 4)
LOG10
LOG10 returns the base-10 logarithm of the specified float expression.
Syntax
LOG10 ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float type expression | 2 |
Return Types
float
Example 1
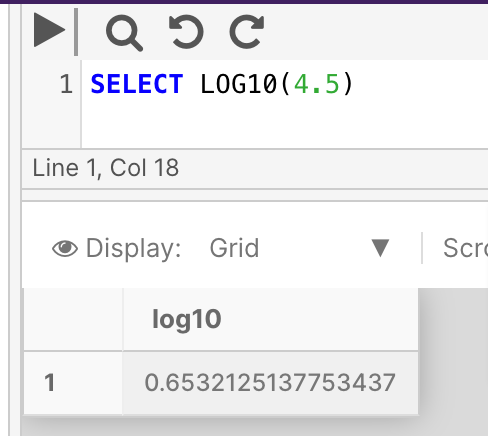
Return the base-10 logarithm of 4.5:
SELECT LOG10(4.5)
Example 2
The following example returns the result of raising a base-10 logarithm to a specified power.
SELECT POWER (10, LOG10(5))
PI
PI returns the constant value of PI.
Syntax
PI ( )
Return Types
float
Example
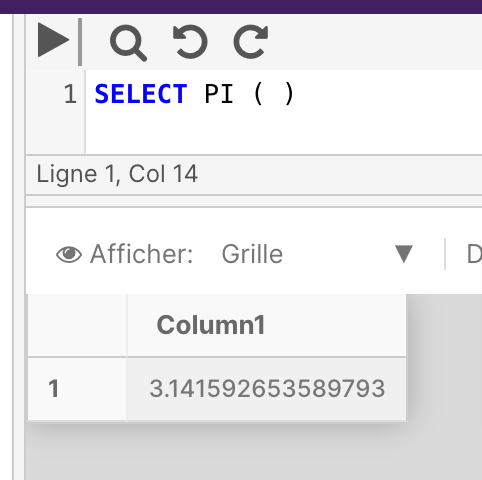
The following example returns the value of PI.
SELECT PI()
POWER
POWER returns the value of the specified expression to the specified power.
Syntax
POWER ( float_expression , y )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float type expression | 4 |
y | The power to which to raise the float_expression. Bit is not supported. | 2 |
Return Types
The return type depends on the input type of float_expression:
| Input type | Return type |
|---|---|
| float, real | float |
| decimal(p, s) | decimal(38, s) |
| int, smallint, tinyint | int |
| bigint | bigint |
| money, smallmoney | money |
| bit, char, nchar, varchar, nvarchar | float |
If the result doesn't fit in the return type, an arithmetic overflow error occurs.
Example
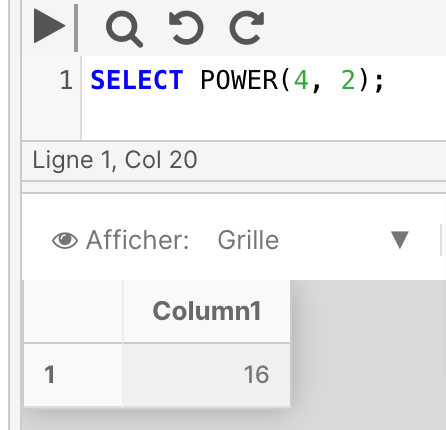
The below example raises 4 to the power of 2.
SELECT POWER (4,2)
RADIANS
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
RADIANS returns radians when a numeric expression, in degrees, is entered.
Syntax
RADIANS ( numeric_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
numeric_expression | A numeric type expression. Bit is not supported. | 130 |
Return Types
Returns the same type as numeric_expression.
Example
SELECT RADIANS(130)
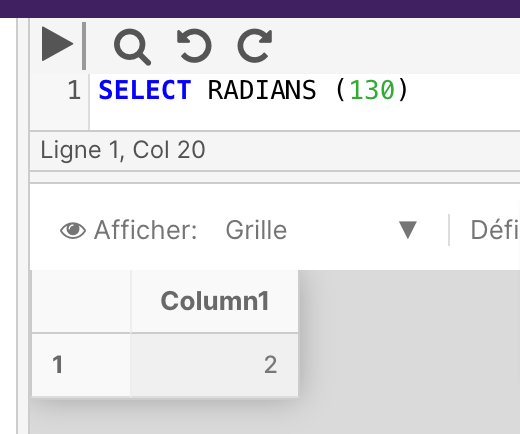
RAND
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
RAND returns a pseudo-random float value from 0 through 1, exclusive.
Syntax
RAND (seed)
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
seed | Is an integer expression (tinyint, smallint, or int) that gives the seed value. If seed isn't specified, a seed value is assigned at random. For a specified seed value, the result returned is always the same. | 100 |
Return Types
float
Remarks
Repetitive calls of RAND() with the same seed value return the same results.
For one connection, if RAND() is called with a specified seed value, all subsequent calls of RAND() produce results based on the seeded RAND() call. For example, the following query will always return the same sequence of numbers.
SELECT RAND(100), RAND(), RAND()
Example
SELECT RAND(100), RAND(), RAND(5)
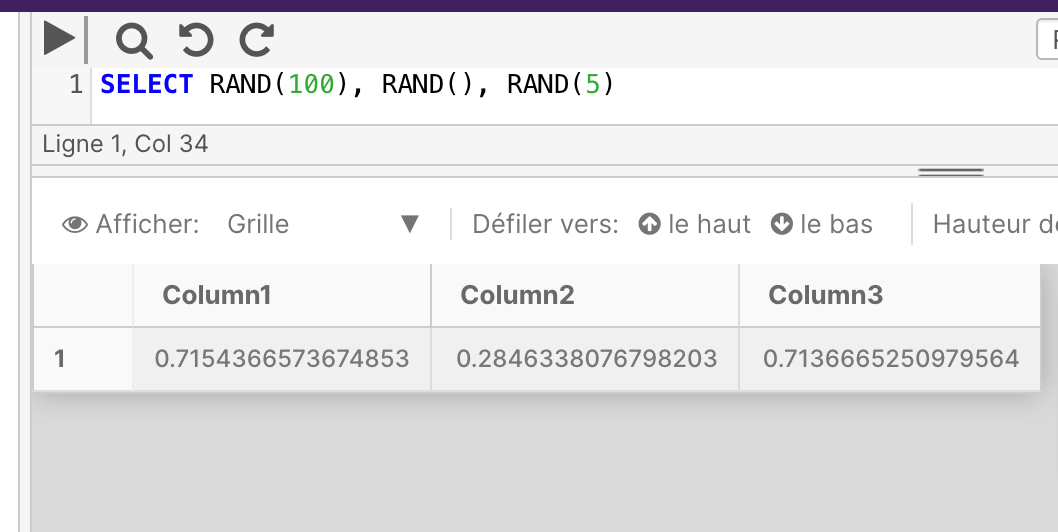
ROUND
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
ROUND returns a numeric value, rounded to the specified length or precision.
Syntax
ROUND ( numeric_expression , length [ ,operation ] )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
numeric_expression | A numeric type expression. Bit is not supported. | 123.449 |
length | The precision for rounding the numeric_expression. It must be an expression of type tinyint, smallint, or int. When length is a positive number, numeric_expression is rounded to the number of decimal positions specified by length. When length is a negative number, numeric_expression is rounded on the left side of the decimal point, as specified by length. | 4 |
operation | Optional. If 0, it rounds the result to the number of decimal. If another value than 0, it truncates the result to the number of decimals. Default value is 0 | 0 |
Return Types
Returns the following data types:
| Expression result | Return type |
|---|---|
| tinyint | int |
| smallint | int |
| int | int |
| bigint | bigint |
| decimal and numeric category (p, s) | decimal(p, s) |
| money and smallmoney category | money |
| float and real category | float |
Example 1
Using ROUND and estimates.
The below example rounds the number 235.415 to 2 decimal places.
SELECT ROUND(235.415, 2, 0)
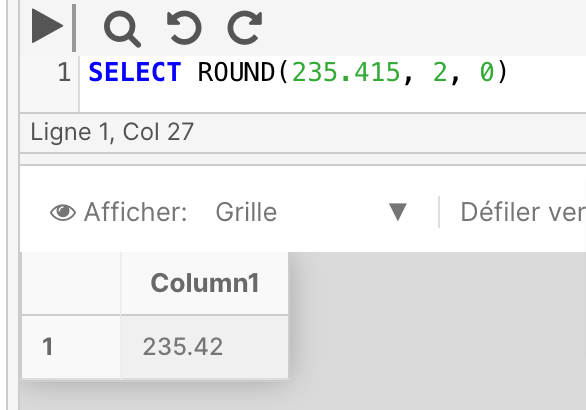
Example 2
Using ROUND to truncate
The following example uses two SELECT statements to demonstrate the difference between rounding and truncation. The first statement rounds the result. The second statement truncates the result.
SELECT ROUND(150.75, 0), ROUND(150.75, 0, 1)
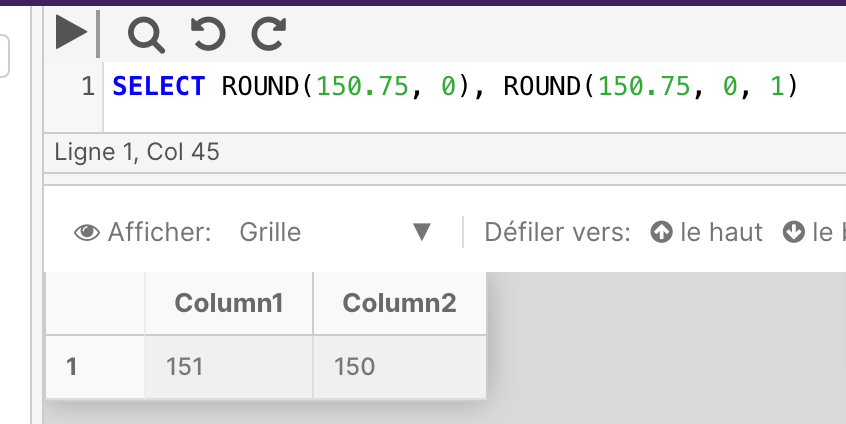
SIGN
SIGN returns a value that denotes whether a numeric expression is positive, negative, or 0.
Syntax
SIGN ( numeric_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
numeric_expression | A numeric type expression. Bit is not supported. | 5 |
Return Types
SIGN returns a 1 for a positive numeric expression, a -1 for a negative numeric expression, or a 0 if the numeric expression is equal to 0.
Example
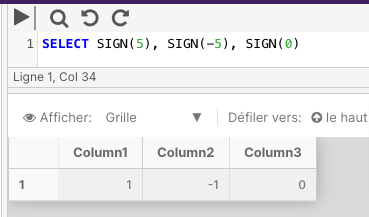
The below example returns the SIGN values of a positive number, negative number, and zero.
SELECT SIGN(5), SIGN(-5), SIGN(0)
SIN
SIN returns the trigonometric sine of the specified angle, in radians, and in an approximate float expression.
Syntax
SIN ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float type expression | 250 |
Return Types
float
Example
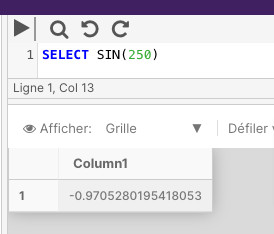
The following example calculates the SIN for a specified angle.
SELECT SIN(250)
SQRT
SQRT returns the square root of the specified float value.
Syntax
SQRT ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float type expression | 81 |
Return Types
float
Example
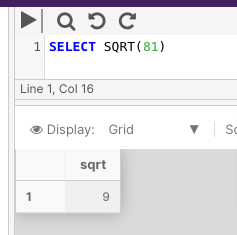
The below example returns the square root of 81.
SELECT SQRT(81)
SQUARE
SQUARE returns the square of the specified float value.
Syntax
SQUARE ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float type expression | 9 |
Return Types
float
Example
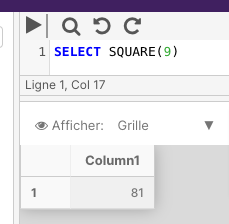
The following example returns the squared result of 9.
SELECT SQUARE(9)
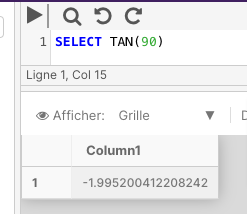
TAN
TAN returns the tangent of the input expression.
Syntax
TAN ( float_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float type expression | 90 |
Return Types
float
Example
The following example returns the tangent of a specified angle.
SELECT TAN(90)