String functions
Overview
The string functions covered in this section perform operations on a string (char or varchar) input value and return a string or numeric value.
- ASCII
- CHAR
- CHARINDEX
- CONCAT
- CONCAT_WS
- DIFFERENCE
- FORMAT
- LEFT
- LEN
- LOWER
- LTRIM
- NCHAR
- PATINDEX
- QUOTENAME
- REPLACE
- REVERSE
- RIGHT
- RTRIM
- SOUNDEX
- SPACE
- STR
- STUFF
- SUBSTRING
- TRANSLATE
- TRIM
- UNICODE
- UPPER
ASCII
ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) returns the ASCII code value of the leftmost (first)character of a character expression.
Return Type
int
Syntax
SELECT ASCII (character)
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
character | An integer, or character expression. | A |
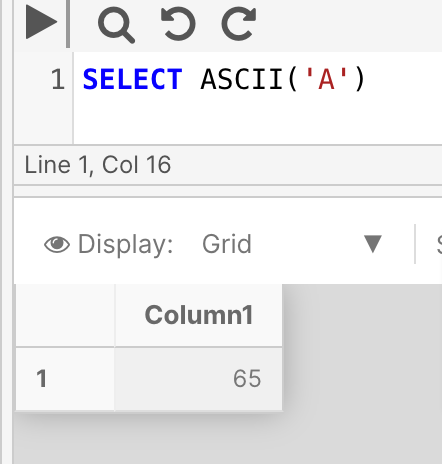
Example 1
The following example returns the ASCII code for the character 'A'.
SELECT ASCII ('A')
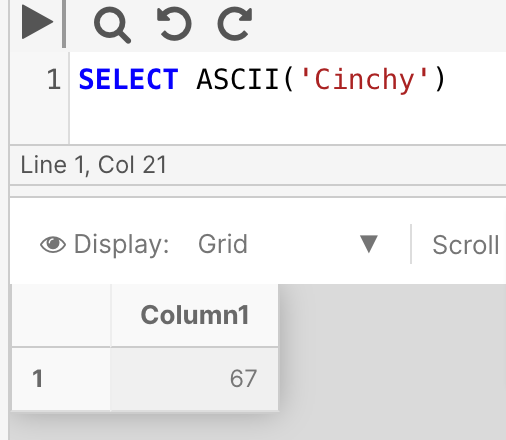
Example 2
The following example returns the ASCII code for the left-most (first) character in the expression 'Cinchy', i.e. 'C'.
SELECT ASCII ('Cinchy')
CHAR
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
CHAR converts an int between 0 to 255 to a character value. Outside of this range, it will return a NULL value.
Syntax
CHAR (integer)
Return Type
char
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
integer | An integer, or integer expression, from 0-255 (inclusive) | 100 |
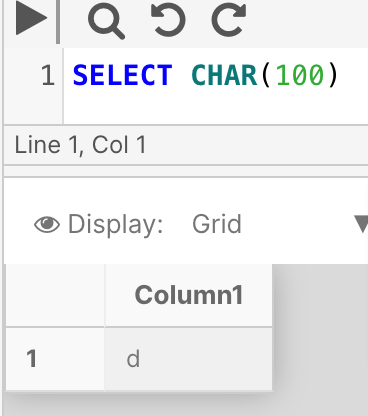
Example 1
The following example converts the integer '100' to a character value.
SELECT CHAR(100)
CHARINDEX
CHARINDEX searches for one character expression inside another character string. If found, the function will return the starting position count of the first instance of the expression. This count includes spaces/blank values.
If CHARINDEX doesn't find the expression within the string, CHARINDEX will return 0.
Syntax
CHARINDEX ( expressionToFind , string [ , start_location ] )
Return Type
int
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expressionToFind | The expression that needs to be found in the ExpressionString | a |
string | The string that contains the expression to find. | this is a beautiful day |
start_Location | Optional. A start location for the search, as in integer, inclusive of spaces/blank values. | 15 |
Example 1
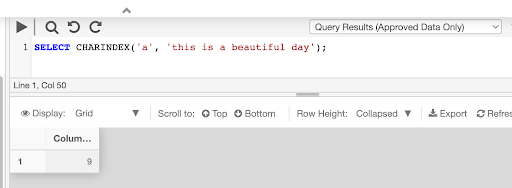
The following example searches the string "this is a beautiful day" and returns the starting position of the expression "a" as an integer.
SELECT CHARINDEX('a', 'this is a beautiful day')
Example 2
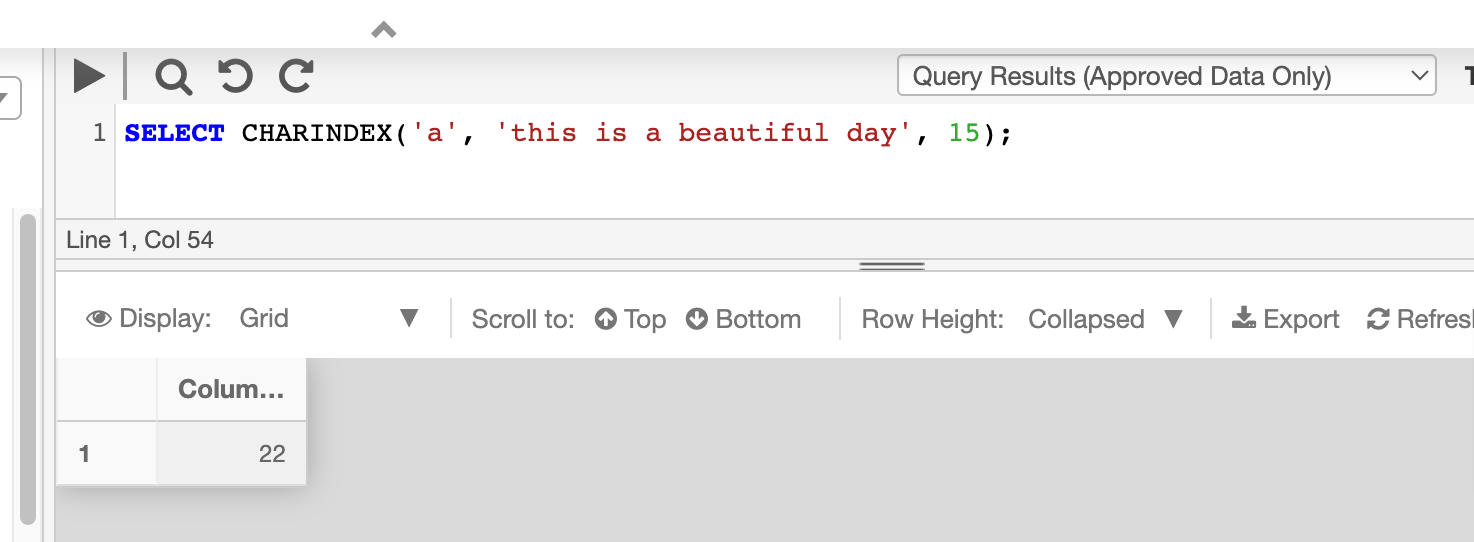
Returning the starting position of an expression with an optional start location. This can be useful in cases where the string contains more than one instance of the expression.
This example searches for a in the string value starting from 15th position.
SELECT CHARINDEX('a', 'this is a beautiful day', 15);
CONCAT
CONCAT concatenates two or more string values one after the other. This function can concatenate at up to 254 strings.
Syntax
CONCAT ( string1, string2 )
Return Type
string
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | A string to concatenate to every other string in the query. You can have up to 254 strings at once. | Happy |
Example
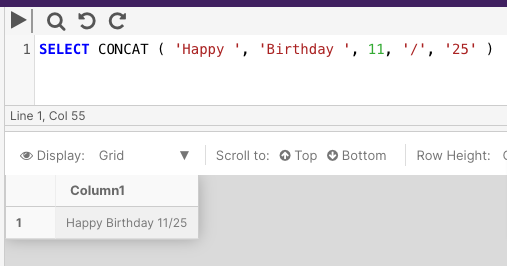
The following example concatenates 5 strings together.
SELECT CONCAT ( 'Happy ', 'Birthday ', 11, '/', '25' )
CONCAT_WS
CONCAT_WS ("concat with separator") returns a string resulting from the concatenation, or joining, of two or more string values in an end-to-end manner. It separates those concatenated string values with the delimiter specified in the first function argument.
Syntax
CONCAT_WS ( separator, string1, string2 )
Return Type
string
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
separator | An expression of any character type (char, nchar, nvarchar, or varchar) tht will serve as a delimiter between the strings. | ' , ' |
string | A string to concatenate to every other string in the query. You can have up to 254 strings at once. | 'Ottawa' |
Example
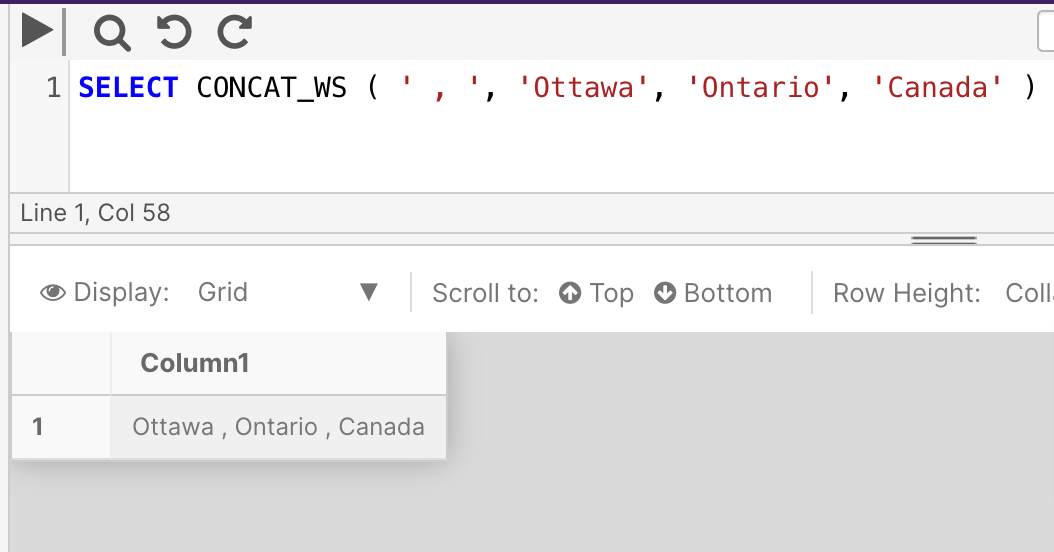
The following example concatenates three strings together and separates them with a ',' delimiter.
SELECT CONCAT_WS ( ',', 'Ottawa', 'Ontario', 'Canada' )
DIFFERENCE
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
DIFFERENCE returns an integer value measuring the difference between the SOUNDEX () values of two different character expressions strings.
Syntax
DIFFERENCE ( string , string )
Return Type
int
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | An alphanumeric expression of character data. This string can be a constant, variable, or a column. | Day |
Example
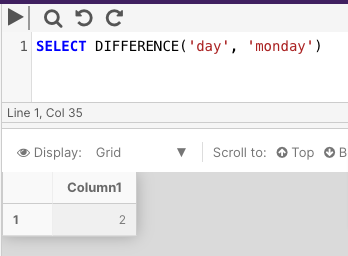
The following example returns an integer value measuring the difference between the SOUNDEX values for day and monday.
SELECT DIFFERENCE('day', 'monday')
FORMAT
FORMAT returns a value formatted in a specific way. Use the FORMAT function for locale-aware formatting of date/time and number values as strings. For general data type conversions, use CAST or CONVERT.
Syntax
FORMAT ( value, format )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
value | A numeric or DATETIME expression. | GETDATE |
format | An nvarchar format pattern. | dd/MM/yyyy |
Remarks
The format argument must contain a valid .NET Framework format string, either as a standard format string (for example, "C" or "D"), or as a pattern of custom characters for dates and numeric values (for example, "MMMM DD, YYYY (DDDD)").
The following table lists the acceptable data types for the value argument together with their .NET Framework mapping equivalent types.
| Category | Type | .NET type |
|---|---|---|
| Numeric | bigint | Int64 |
| Numeric | int | Int32 |
| Numeric | smallint | Int16 |
| Numeric | tinyint | Byte |
| Numeric | decimal | SqlDecimal |
| Numeric | numeric | SqlDecimal |
| Numeric | float | Double |
| Numeric | real | Single |
| Numeric | smallmoney | Decimal |
| Numeric | money | Decimal |
| Date and Time | date | DateTime |
| Date and Time | time | TimeSpan |
| Date and Time | datetime | DateTime |
| Date and Time | smalldatetime | DateTime |
| Date and Time | datetime2 | DateTime |
| Date and Time | datetimeoffset | DateTimeOffset |
Return types
nvarchar
Example 1
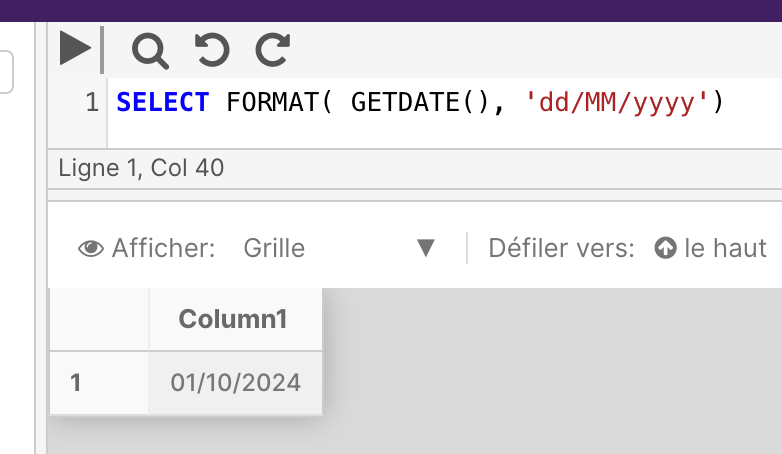
The following example shows formatting date values by specifying a custom format.
SELECT FORMAT( GETDATE(), 'dd/MM/yyyy')
Example 2
The following example shows formatting numeric values by specifying a custom format.
SELECT FORMAT(123456789,'###-##-####') AS 'Numeric Format'
LEFT
LEFT returns a specified number of characters from the left part of a character string.
Syntax
LEFT ( string , integer )
Return type
string
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | An expression of character or binary data. It can be of any data type, except text or ntext, that can be implicitly converted to varchar or nvarchar. | abcdefghi |
integer | A positive integer that specifies how many characters of the string will be returned. | 2 |
Example
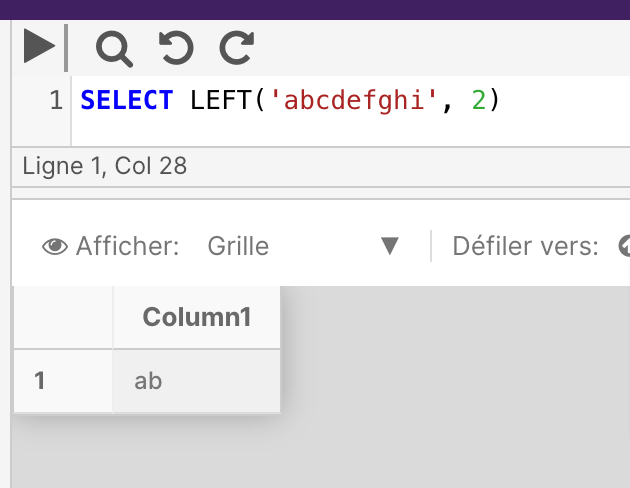
The following example returns the two leftmost characters from the string.
SELECT LEFT('abcdefghi', 2)
LEN
LEN returns the number of characters of the specified string expression, excluding trailing spaces.
Syntax
LEN ( string )
Return types
bigint if expression is of the varchar(max), nvarchar(max) or varbinary(max) data types; otherwise, int.
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | A string expression | abcde |
Example
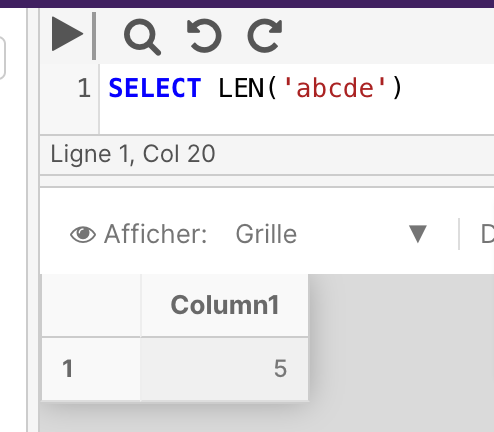
The below example returns the number of characters in the string abcde.
SELECT LEN('abcde')
LOWER
LEN returns a character expression after converting uppercase character data to lowercase.
Syntax
LOWER ( expression )
Return types
varchar or nvarchar
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | A string or binary data expression | ABCdef |
Example
SELECT LOWER('ABCdef')
LTRIM
LTRIM returns a character expression after it removes any leading blanks.
Syntax
LTRIM ( expression )
Return types
varchar or nvarchar
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | A string or binary data expression | Remove leading spaces. |
Example
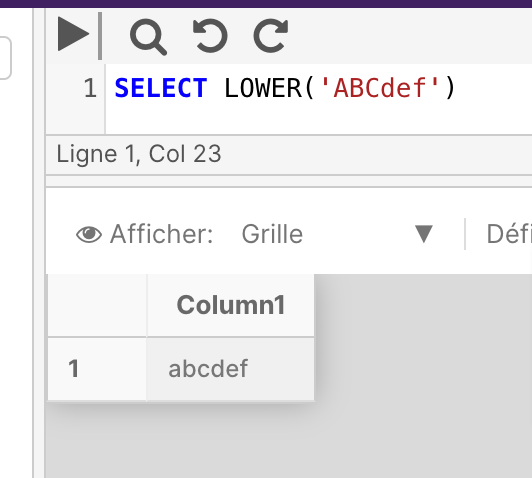
The following example uses LTRIM to remove leading spaces from a string
SELECT LTRIM(' Remove leading spaces.')
NCHAR
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
NCHAR returns the Unicode character with the specified integer code, as defined by the Unicode standard.
Syntax
NCHAR (expression)
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | A positive integer with a value from 0 through 65535 | 87 |
Example
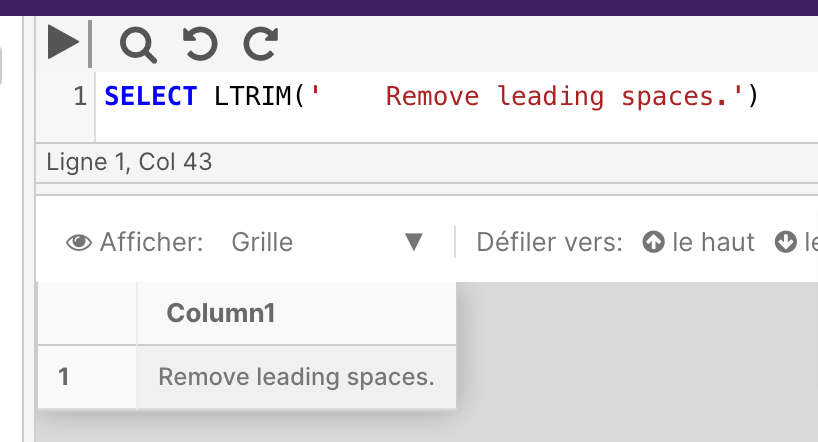
This example returns the unicode character for '87'.
SELECT NCHAR(87)
PATINDEX
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
PATINDEX returns the starting position of the first occurrence of a pattern in a specified expression.
Syntax
PATINDEX ( '%pattern%' , expression )
Return types
int or bigint
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
%pattern% | A character expression containing the sequence to be found. Wildcard characters can be used; however, the % character must come before and follow pattern. | %eat% |
expression | A string expression that's searched for the specified pattern. | this is a great day |
Example
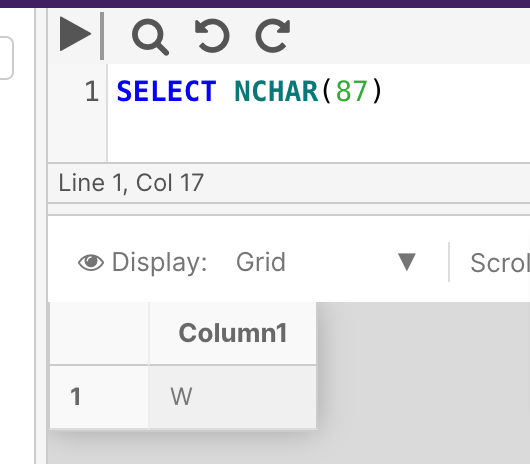
The following example checks a short character string (this is a great day) for the starting location of the characters eat.
SELECT PATINDEX('%great%', 'this is a great day')
QUOTENAME
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
QUOTENAME returns a Unicode string with the delimiters added to make the input string a valid SQL Server delimited identifier.
Syntax
QUOTENAME ( 'character_string' [ , 'quote_character' ] )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
character_string | A string of Unicode character data, no greater than 128 characters. | abc[]def |
quote_character | A one-character string to use as the delimited. Can be a single quotation mark ( ' ), a left or right bracket ( [] ), a double quotation mark ( " ), a left or right parenthesis ( () ), a greater than or less than sign ( >< ), a left or right brace ( ) or a backtick ( ` ). NULL returns if an unacceptable character is supplied. If quote_character is not specified, brackets are used. | " |
Example
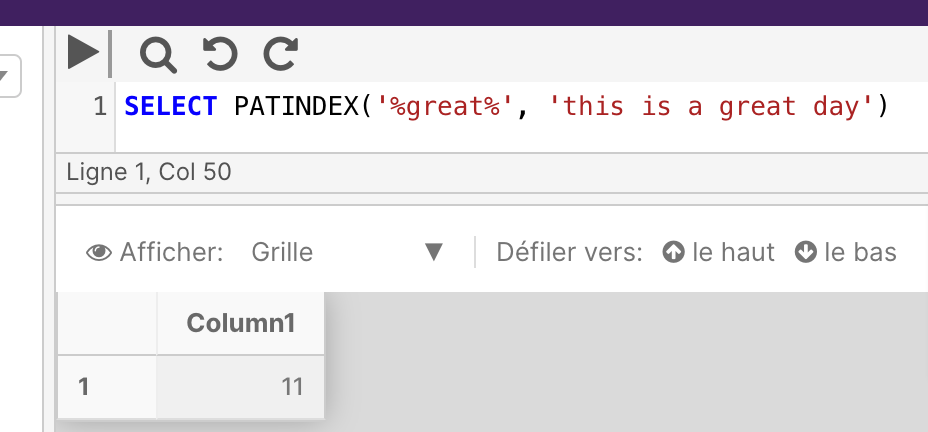
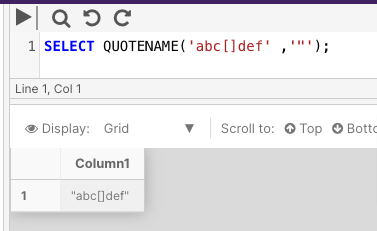
The following example takes the character string abc[]def and uses a " delimiter.
SELECT QUOTENAME('abc[]def' ,'"');
REPLACE
REPLACE replaces all occurrences of a specified string value with another string value.
Syntax
REPLACE ( string , string_toBeReplaced , string_replacedBy )
Return types
Returns nvarchar if one of the input arguments is of the nvarchar data type; otherwise, REPLACE returns varchar
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | The string expression to be searched. | 10/09/1995 |
string_toBeReplaced | The string expression to be found. | 10 |
string_replacedBy | The replacement string. | October |
Example
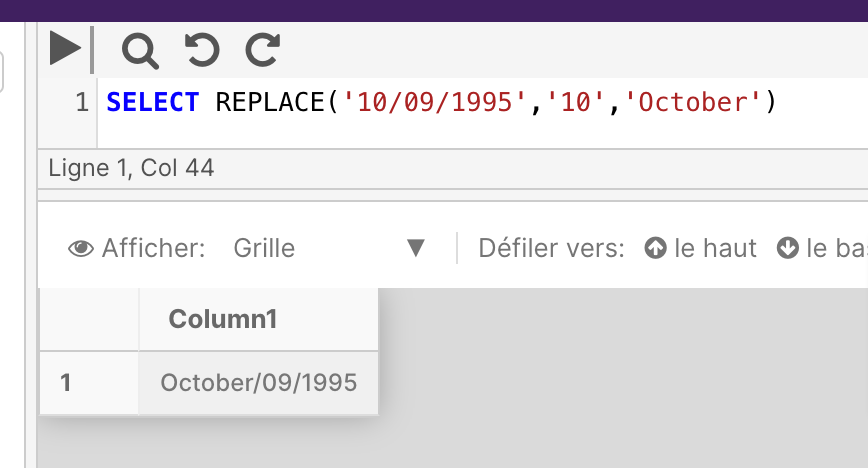
The following example replaces the string cde in abcdefghi with xyz.
SELECT REPLACE('10/09/1995','10','October')
REPLICATE
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
REPLICATE repeats a string value a specified number of times.
Syntax
REPLICATE ( string_expression , integer_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string_expression | A character or binary string to be replicated. | abcd |
integer_expression | An integer representing the amount of times the string_expression will be replicated. | 4 |
Example
The following example replicates 'abcd' four times.
SELECT REPLICATE ( 'abcd' , 4 )
REVERSE
REVERSE returns the reverse order of a string value.
Syntax
REVERSE ( string )
Return types
varchar or nvarchar
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | A string or binary expression. | 123456789 |
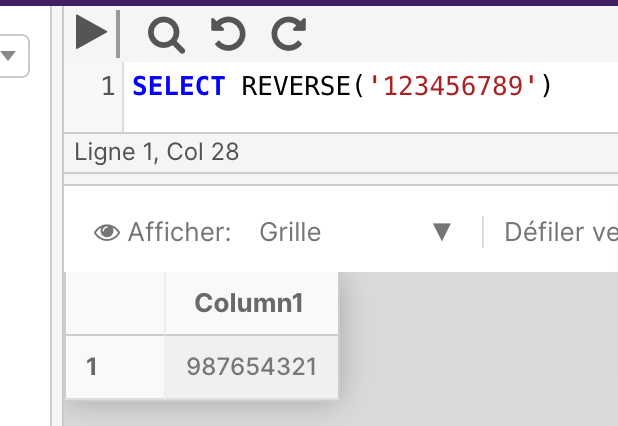
Example
SELECT REVERSE('123456789')
RIGHT
RIGHT returns the right part of a character string with the specified number of characters.
Syntax
RIGHT ( string , integer )
Return type
Returns varchar when character_expression is a non-Unicode character data type.
Returns nvarchar when character_expression is a Unicode character data type.
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | An expression of character or binary data. | abcdefghi |
integer | A positive integer that specifies how many characters of the string will be returned. | 2 |
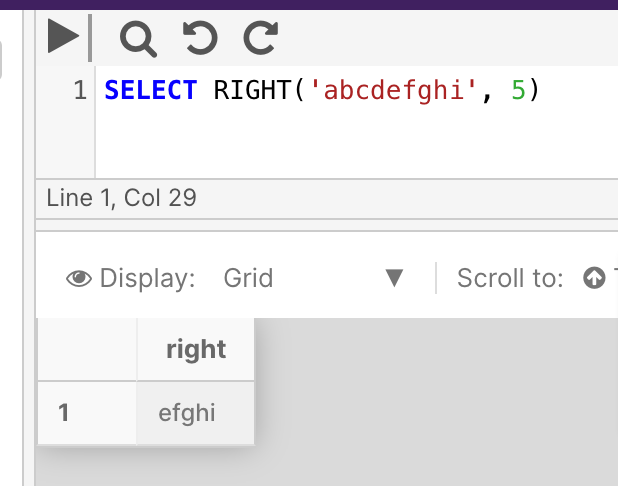
Example
SELECT RIGHT('abcdefghi', 5)
RTRIM
RTRIM returns a character string after truncating all trailing spaces.
Syntax
RTRIM ( string )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | A string expression. | Removes trailing spaces. |
Return types
varchar or nvarchar
Example
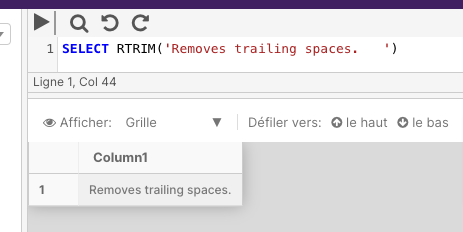
The below example removes the trailing spaces from the end of the string.
SELECT RTRIM('Removes trailing spaces. ')
SOUNDEX
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
SOUNDEX returns a four-character (SOUNDEX) code to evaluate the similarity of two strings.
SOUNDEX converts an alphanumeric string to a four-character code that's based on how the string sounds when spoken.
Syntax
SOUNDEX ( string )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | A string expression. | Canada |
Return types
varchar
Example
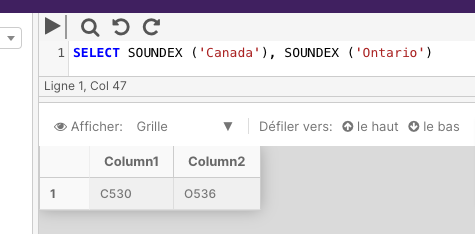
The below example returns the SOUNDEX value of the strings Canada and Ontario.
SELECT SOUNDEX ('Canada')
SPACE
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
SPACE returns a string of repeated spaces.
Syntax
SPACE ( integer_expression )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
integer_expression | A positive integer that indicates the number of spaces. | 2 |
Return types
varchar
Example
The below example concatenates a comma, two spaces, and the first/last names.
SELECT 'John' + ',' + SPACE(2) + 'Doe'
Whitespace collapse in the Query Builder UI means that results returned in the grid may not display the added spacing. This is simply UI behaviour, and does not impact the actual data. To confirm whether your spacing was added correctly, copy and paste the cell out of the query builder.
STR
STR returns character data converted from numeric data. The character data is right-justified, with a specified length and decimal precision.
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
Syntax
STR ( float_expression [ , length [ , decimal ] ] )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
float_expression | A float expression with a decimal point. | 345.62 |
length | The total length of the data, including decimal point, sign, digits, and spaces. The default length when unspecified is 10. | 6 |
decimal | The number of places returned to the right of the decimal point. This value must be less than or equal to 16. | 1 |
Return types
varchar
Example
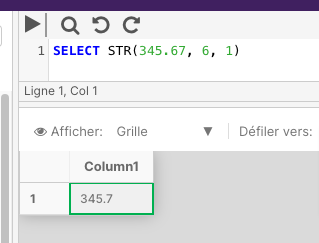
The following example converts an expression that's made up of five digits and a decimal point to a six-position character string. The fractional part of the number is rounded to one decimal place.
SELECT STR(345.67, 6, 1)
STUFF
STUFF inserts a string into another string. It deletes a specified length of characters in the first string at the start position and then inserts the second string into the first string at the start position.
Syntax
STUFF ( string , start , length , replaceWith )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | A string expression. | string |
start | An integer value that specifies the location to start the deletion/insertion. | 4 |
length | An integer value that specifies the number of characters to delete. | 1 |
replaceWith | An expression that will be inserted at the start position. | u |
Example
The following example returns a character string created by deleting one character from the first string, String, starting at position 4, at i, and inserting the second string, u, at the deletion point.
SELECT STUFF('string', 4, 1, 'u')
SUBSTRING
SUBSTRING returns part of a character, binary, or text expression.
Syntax
SUBSTRING ( expression , start , length )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
expression | Is a character, binary,oor text expression. | Rahul |
start | An integer value that specifies the location where the returned characters start. | 1 |
length | An integer value that specifies the number of characters from the expression that will be returned. | 1 |
Example
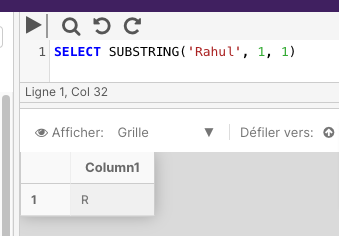
The below example returns the first letter of the name.
SELECT SUBSTRING('Rahul', 1, 1)
TRANSLATE
This function translates a specified character/set of characters in a string and returns a new string.
Syntax
TRANSLATE ( string, characters, translations )
Arguments
| Argument | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
string | A string expression that contains the characters to be translated. | 2*[3+4]/{7-2} |
characters | A string expression that defines which characters should be replaced in the above string. | [] |
translations | A string expression that defines how the above characters should be translated within thee string. | ()() |
Example 1
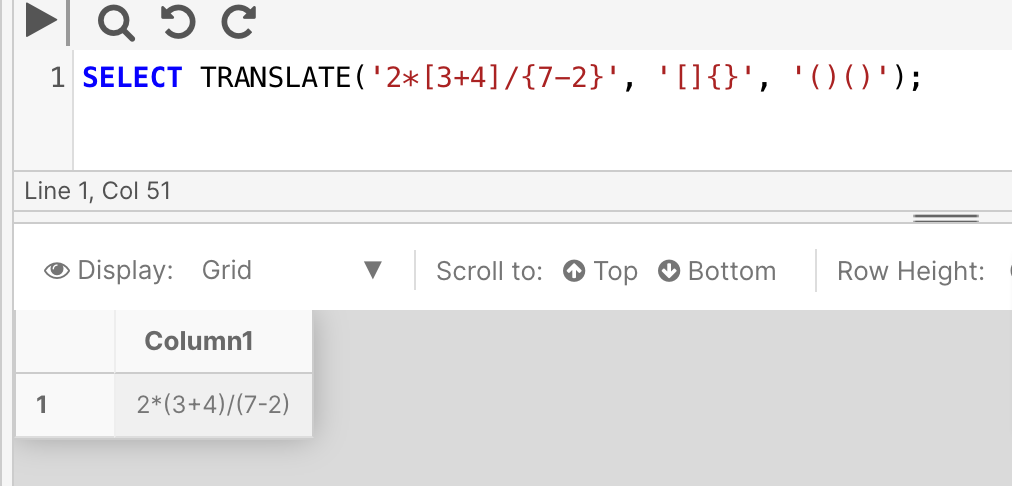
The following example tells the query to translate twice: [] should become (), and should also become (). Note how even though the translations expressions are the same, they still need to be included twice (one translation expression for each character expression.)
SELECT TRANSLATE('2*[3+4]/{7-2}', '[]{}', '()()')
TRIM
TRIM removes the space character or other specified characters from the start and end of a string.
Syntax
TRIM ( [ characters FROM ] string )
Arguments
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
string | A string expression that contains white spaces or characters to be trimmed. |
characters FROM | By default, TRIM will remove trailing and leading whitespaces. If there are other (trailing and leading) characters that you want trimmed, you can define them here as well. |
Example 1
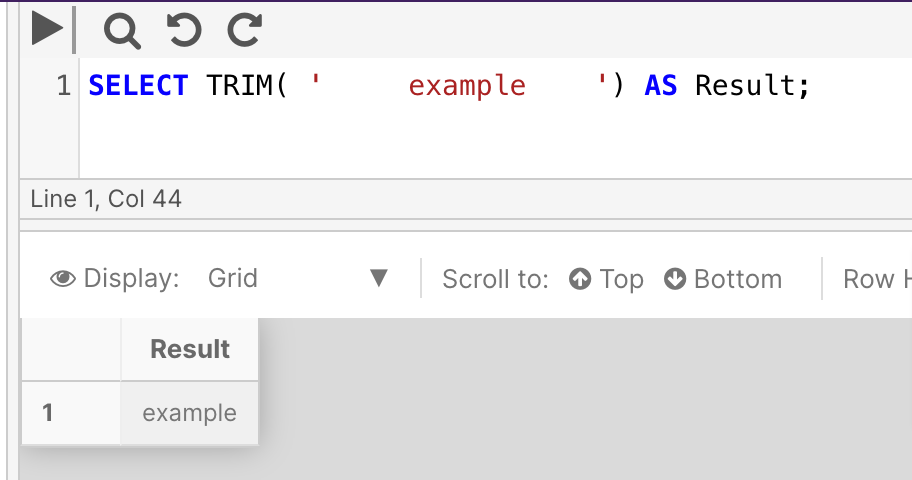
The following example trims the white space around the word 'example' and returns the results.
SELECT TRIM( ' example ')
Example 2
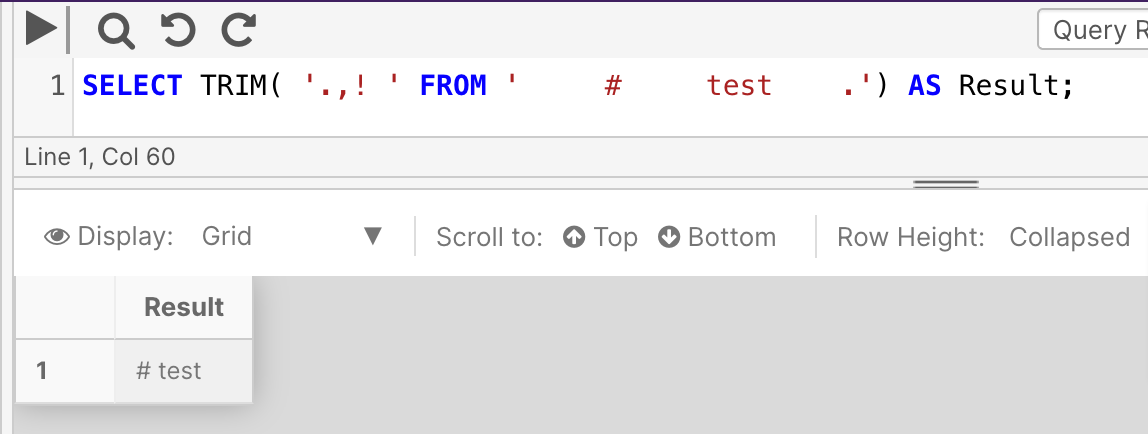
The following example defines extra characters, '.,! ' to be trimmed. Only the trailing period and spaces from before # and after the word test were removed. The other characters were ignored because they didn't exist in the string.
SELECT TRIM( '.,! ' FROM ' # test .') AS Result;
UNICODE
This function isn't currently supported in PostgreSQL deployments of the Cinchy platform.
New function translations are actively being worked on by the development team; please check back at a later time.
You can review the full list of in-progress function translations here.
UNICODE returns the integer value, as defined by the Unicode standard, for the first character of the input expression.
Syntax
UNICODE ( 'ncharacter_expression' )
Arguments
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
ncharacter_expression | A character expression of nchar or nvarchar type. |
Example
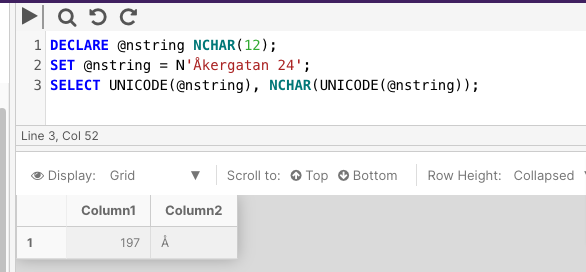
The following example uses the UNICODE and NCHAR functions to print the UNICODE value of the first character of the string Åkergatan 24, and to print the actual first character, Å.
DECLARE @nstring NCHAR(12);
SET @nstring = N'Åkergatan 24';
SELECT UNICODE(@nstring), NCHAR(UNICODE(@nstring));
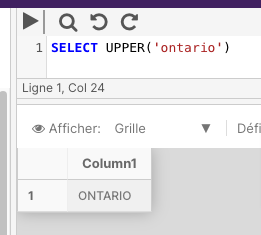
UPPER
UPPER returns a character expression with lowercase character data converted to uppercase.
Syntax
UPPER ( string )
Return types
varchar or nvarchar
Arguments
| Argument | Description |
|---|---|
string | A string expression. |
Example
The following example uses the UPPER function to return the name in uppercase.
SELECT UPPER('ontario')