Binary file
Overview
A binary file is a computer file that's not a text file, and whose content is in a binary format consisting of a series of sequential bytes, each of which is eight bits in length.
You can use binary files from a Local upload, Amazon S3, or Azure Blob Storage in your data syncs.
Some benefits of using binary files include:
- Better efficiency via compression
- Better Security through the ability to create custom encoding standards.
- Unmatched Speed, since the data is stored in a raw format, and isn't encoded using any character encoding standards, it's faster to read and store.
Example use case
You have a binary file that contains your Employee information. You want to use a batch sync to pull this info into a Cinchy table and liberate your data.
The Binary File source supports batch syncs.
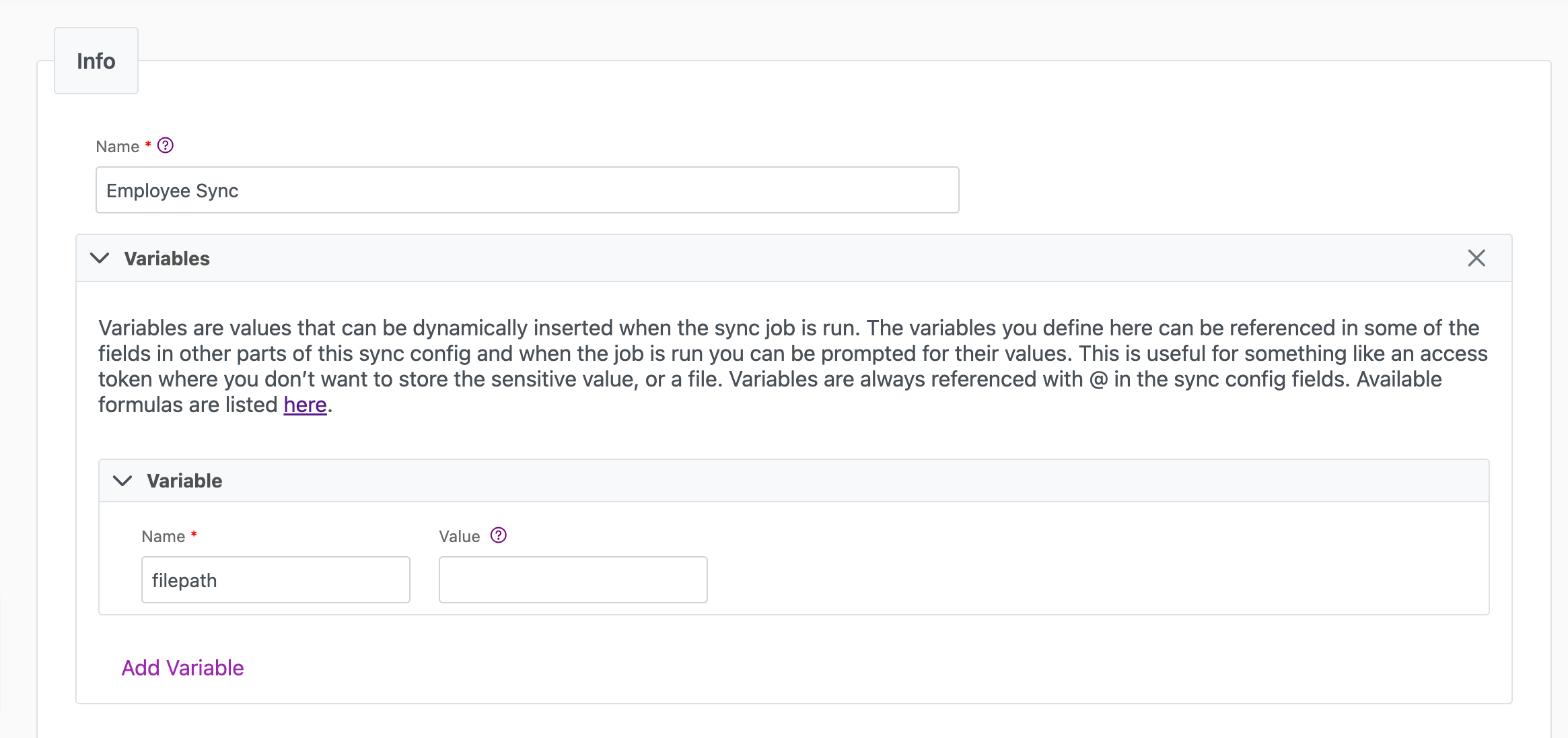
Info tab
You can find the parameters in the Info tab below (Image 1).
Values
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Title | Mandatory. Input a name for your data sync | Employee Sync |
| Variables | Optional. Review our documentation on Variables herefor more information about this field. When uploading a local file, set this to filepath. | @Filepath |
| Permissions | Data syncs are role based access systems where you can give specific groups read, write, execute, and/or all of the above with admin access. Inputting at least an Admin Group is mandatory. |
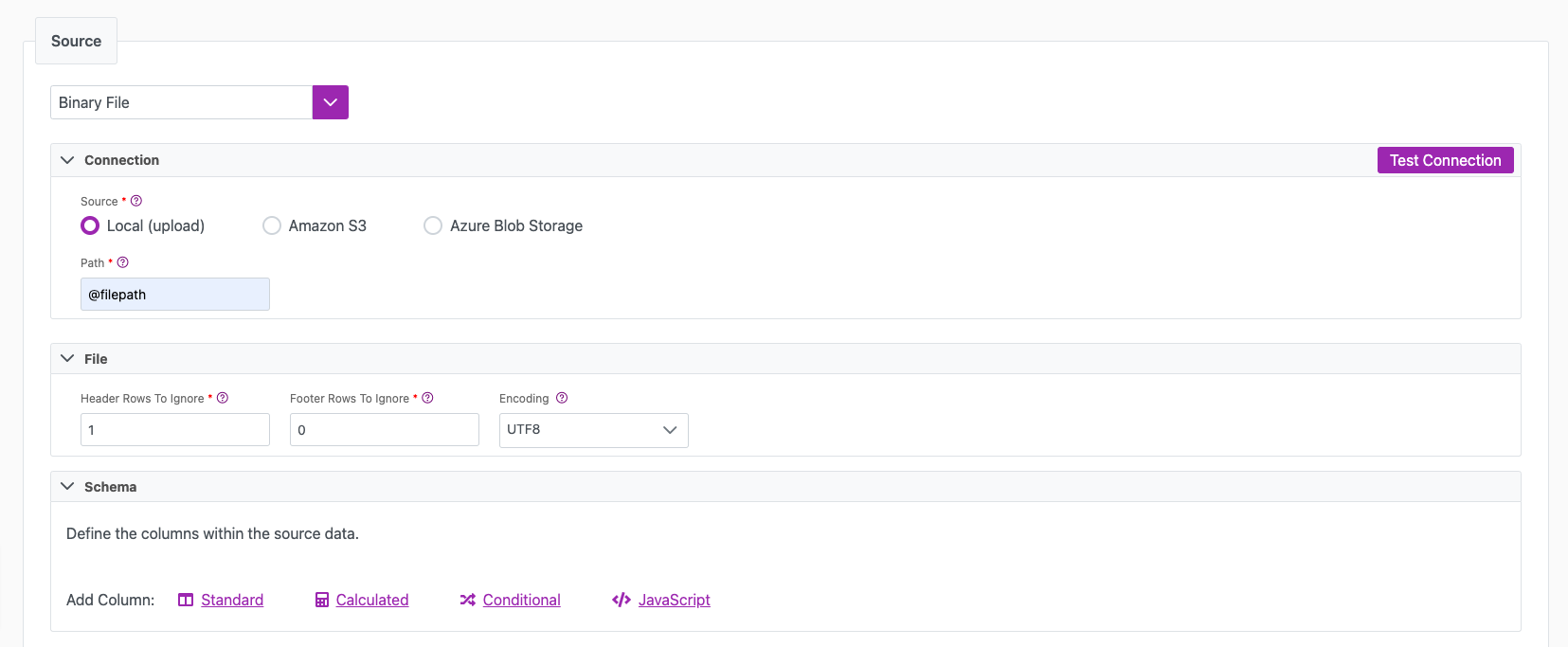
Source tab
The following table outlines the mandatory and optional parameters you will find on the Source tab (Image 2).
- Source Details
- Schema
- Filter
The following parameters will help to define your data sync source and how it functions.
For information on setting up registered applications for S3 or Azure, please see the Registered Applications page.
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| (Sync) Source | Mandatory. Select your source from the drop down menu. | Binary File |
| Source | Mandatory. The location of the source file. Either a Local upload, Amazon S3, or Azure Blob Storage. The following authentication methods are supported per source: - Amazon S3: Access Key ID/Secret Access Key - Azure Blob Storage: Connection String | Local |
| Header Rows to Ignore | Mandatory. The number of records from the top of the file to ignore before the data starts (includes column header). For example, setting this value to 1 will ignore the top data row, which might be a header row that you do not want to sync. | 1 |
| Footer Rows to Ignore | Mandatory. The number of records from the bottom of the file to ignore. For example, setting this value to 1 will ignore the bottom data row, which might be a footer row that you do not want to sync. | 0 |
| Encoding | Optional. The encoding of the file. This default to UTF8, however also supports: UTF8_BOM, UTF16, ASCII. | |
| Path | Mandatory. The path to the source file to load. To upload a local file, you must first insert a Variable in the Info tab of the connection (ex: filepath). Then, you would reference that same value in this location (Ex: @Filepath). This will trigger a File Upload option to import your file. | @Filepath |
| AuthType | Mandatory. when using Amazon S3 or Azure Blob Storage. This field defines the authentication type for your data sync. Cinchy supports "Access Key" and "IAM" role. When selecting Access Key, you must provide the key and key secret. When selecting IAM role, a new field will appear for you to paste in the role's Amazon Resource Name (ARN). You also must ensure that the role must be configured to have at least read access to the source. The Connections pods' role must have permission to assume the role specified in the data sync config. | |
| Test Connection | You can use the "Test Connection" button to ensure that your credentials are properly configured to access your source. If configured correctly, a "Connection Successful" pop-up will appear. If configured incorrectly, a "Connection Failed" pop-up will appear along with a link to the applicable error logs to help you troubleshoot. |
The Schema section is where you define which source columns you want to sync in your connection. You can repeat the values for multiple columns.
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Mandatory. The name of your column as it appears in the source. | Name |
| Alias | Optional. You may choose to use an alias on your column so that it has a different name in the data sync. | |
| Data Type | Mandatory. The data type of the column values. | Text |
| Description | Optional. You may choose to add a description to your column. | |
| Parse Content By (Only for Standard Columns) | Binary File sources have a unique, mandatory parameter for Standard Columns: Parse Content By - Choose from the following three options to define how you want to parse your content:
| Byte Length |
Select Show Advanced for more options for the Schema section.
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Mandatory |
| |
| Validate Data |
| |
| Trim Whitespace | Optional if data type = text. For Text data types, you can choose whether to trim the whitespace._ | |
| Max Length | Optional if data type = text. For Text data types, you can choose whether to trim the whitespace._ |
You can choose to add in a Transformation > String Replacement by inputting the following:
| Parameter | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Pattern | Mandatory if using a Transformation. The pattern for your string replacement. | |
| Replacement | What you want to replace your pattern with. |
Note that you can have more than one String Replacement. For details on String Replacements, see the documentation here
You have the option to add a source filter to your data sync. Please review the documentation here for more information on source filters.
Next steps
- Configure your Destination.
- Define yourSync Actions.
- Add in your Post Sync Scripts, if required.
- Click Jobs > Start a Job to begin your sync.